Offers in: Electrical Engineering
Academic supervisor:
Juan Ignacio Sancho Seuma
CEITTecnundepartment :
Tecnun: department Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Description and Objectives:
This project use easy-to-learn numerical methods software (CST Studio Suite) to simulate ground grids. The results for conventional grids and soils can be compared with those corresponding to rules and regulations (Standard 80). Based on these values, we will analyze the effect of complex soils, ground grid oxidation, weld deterioration, lightning, and other factors.
Academic supervisor:
Ibon Elósegui Simón
CEITTecnundepartment :
Tecnun: department Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Description and Objectives:
This project an innovative solution: direct oil cooling by jet impingement on subject conductors, applied to high power density electric machines.
Using CFD simulation, we analyze how to optimize heat transfer in electric motors that will power sustainable vehicles and aircraft, reducing losses and increasing reliability.
The results will serve as a basis for the design more efficient cooling systems, contributing to the electrification of air and ground transportation.
Academic supervisor:
José Martín Echeverría Ormaechea
CEITTecnundepartment :
CEIT: Transportation and Energy Division
area :
Power Electronics, Piezoelectric Actuators, Nanometric Positioning
Description and Objectives:
Piezoelectric actuators used in high-precision positioning systems require power stages capable of supplying high voltages—typically between 100 V and 150 V—and transient currents associated with their predominantly capacitive nature. Although commercial controllers exist for this subject actuator, many have closed and limited configurations that make it difficult to optimize their performance or incorporate new specific functionalities.
The goal of project develop and validate a complete power electronics system that allows for the precise and safe excitation of piezoelectric actuators intended for positioning applications. The system must generate programmable control signals (unipolar or bipolar), operate over voltage ranges suitable for different types of actuators, and provide a dynamic response that allows for the evaluation of both the static and transient behavior of the device.
The power stage will include:
-
Implementation of voltage conversion stage to levels suitable for piezoelectric excitation (e.g., boost, flyback, or high-voltage linear power supply topologies).
-
amplification stage design capable of supplying reactive current and maintaining the linearity required for precision applications.
-
Implementation of control and modulation systems necessary to generate ramps, dynamic profiles, or sinusoidal test signals.
-
Internal sensing and monitoring of core topic parameters, such as applied voltage, instantaneous current, or system temperature.
This project students to delve deeper into the design high-voltage power converters, precision analog electronics, capacitive load control, and protection techniques, result fully functional and documented piezoelectric module .
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcarcel Garcia / Cristina Rodriguez
department Tecnun CEITTecnun:
CEIT - ICT Division / PTM
subjectarea :
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science, Materials.
Description and Objectives:
development of a robust software application (preferably in Python) for parameter optimization of material constitutive equations (known models in the literature).
The goal is to automate the task of fitting models to experimental data (read from Excel/CSV) to predict mechanical properties. It is required to compare different optimization algorithms to determine the best fitting strategy. The project should be integrated or be the basis of an existing application.
Proposed Activities:
-
Literature review of constitutive models and optimization algorithms.
-
Mathematical formulation of the optimization problem (error function).
-
Implementation of data reading (Excel/CSV) and constitutive equations.
-
Implementation and comparison of at least two optimization algorithms (e.g., Levenberg-Marquardt vs. Genetic Algorithms).
-
development the Username interface for loading, adjustment and display of results.
-
Validation and analysis of the effectiveness of the software and algorithms applied.
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcárcel García
department Tecnun CEIT:
ICT Division
subjectarea :
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science
Description and Objectives:
development of a Python application to automate exploratory data analysis (EDA) and predictive regression modeling.
The goal is to build a tool able to read a database (CSV/SQL), automatically classify variables (numerical, categorical), perform univariate and bivariate statistical studies (correlations, graphs) and, finally, automatically apply and compare regression models for a variable of interest. The goal is to offer a robust software for the quick start of Data Science projects.
Proposed Activities:
-
Review of AutoEDA and AutoRegression techniques.
-
Intake module : Data reading and automatic classification of variables.
-
EDA module : Implementation of statistical studies and automatic graphs (univariate and relationship between variables).
-
Regression module : Automatic preprocessing and fitting/comparison of multiple regression algorithms (simplified AutoML).
Username interface: development of an interface (e.g., Shiny) for the visualization of results and insights.
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcárcel García
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT - ICT Division
area subject:
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science
Description and objectives:
The maintenance scheduling problem, known as the Maintenance Scheduling Problem or Maintenance Scheduling Problem, consists of organizing maintenance activities within a schedule in an optimal manner. This problem seeks to minimize interruptions and operating costs by ensuring that both preventive and corrective maintenance are performed at the appropriate times.
The goal of this final Degree project is to develop an optimization tool that addresses the efficient scheduling of maintenance schedules. The tool will be developed preferably in Python, with additional Matlab or R options.
Proposed activities for the student:
Bibliographic review of the most common optimization problems and algorithms applied in maintenance scheduling.
2. Mathematical formulation of the problem, establishing the relevant criteria and restrictions.
3. Implementation of the solution using a heuristic optimization algorithm or open source solvers.
4. Analysis of results and comparison of the effectiveness of the applied approach , with recommendations for its use in different maintenance situations.
Academic Supervisor:
Dr. Emilio Sánchez Tapia
department CEITTecnun:
CEIT - Vision and Robotics
subjectarea :
Industrial automation/robotics
Description and objectives:
This Degree final project is born as a direct continuation of a previous work in which the same unscrewing operation was successfully automated. In that first phase, the control architecture was based on a traditional industrial system, using a PLC to govern the KUKA robot. Having validated the mechanical and vision feasibility of the system, this new project focuses on exploring an alternative and more flexible control architecture.
The new goal is therefore to approach the control from two different perspectives in order to compare its performance. Instead of using the PLC, a specialized controller, extremely reliable and designed to operate in real time, the same process will be implemented using ROS (Robot Operating System) on a conventional computer. ROS is not an operating system like Windows, but a set of open source software tools that greatly facilitates the programming of robots and the integration of components such as cameras or artificial intelligence algorithms. The final scope is to evaluate and quantify the advantages and disadvantages of each approach: the robustness and determinism of the industrial PLC versus the flexibility, speed of development and processing power offered by a system based on ROS and a PC.
Tasks to be performed by the student:
-
Familiarization with previous work
-
Learning the programming technique of the Kuka Issy robot.
-
Learning to use the ROS operating system
-
Programming from ROS of the execution of a sequence of paths for screwing/unscrewing (language to be defined, it can be in Python or C++).
-
Testing and evaluation of the performance achieved
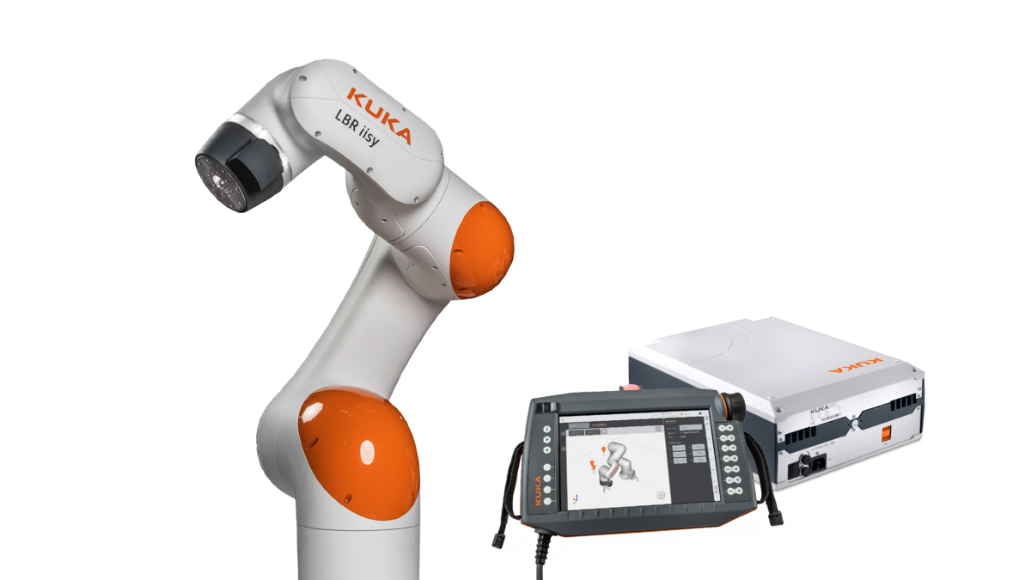

Photo of the KUKA collaborative robot to be used in the PFG.
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcárcel García
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
ICT Division. Group of data analysis and Information Management
area subject:
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science
Description and objectives:
The maintenance scheduling problem, known as the Maintenance Scheduling Problem, consists of optimally organizing maintenance activities within a schedule. This problem seeks to minimize interruptions and operating costs, ensuring that both preventive and corrective maintenance are performed at the right times.
The goal of this end of Degree project is to develop an optimization tool that addresses efficient scheduling of maintenance schedules. The tool will be developed preferably in Python, with additional Matlab or R options.
Proposed student activities:
-
Bibliographic review of the most common optimization problems and algorithms applied in maintenance scheduling.
-
Mathematical formulation of the problem, establishing the relevant criteria and restrictions.
-
Implementation of the solution using a heuristic optimization algorithm or open source solvers.
-
Analysis of results and comparison of the effectiveness of the applied approach , with recommendations for its use in different maintenance situations.
Academic Supervisor:
Emilio Sanchez Tapia
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
Materials and Manufacturing Division: Robotics and Industrial Control Group.
area thematic:
Robotic Engineering
Description and objectives:
In the context of robotics in the 21st century, the concept of the connected factory arises where machines, mobile robots and humans coexist. Mobile robots may or may not include a robotic manipulator arm or MoMa (MObile MAnipulator). If there is only the mobile robot, it is usually referred to as AMR (Autonomous Mobile Robot) or AGV (Autonomous Guide Vehicle) according to its Degree of freedom in navigation (see figure below).
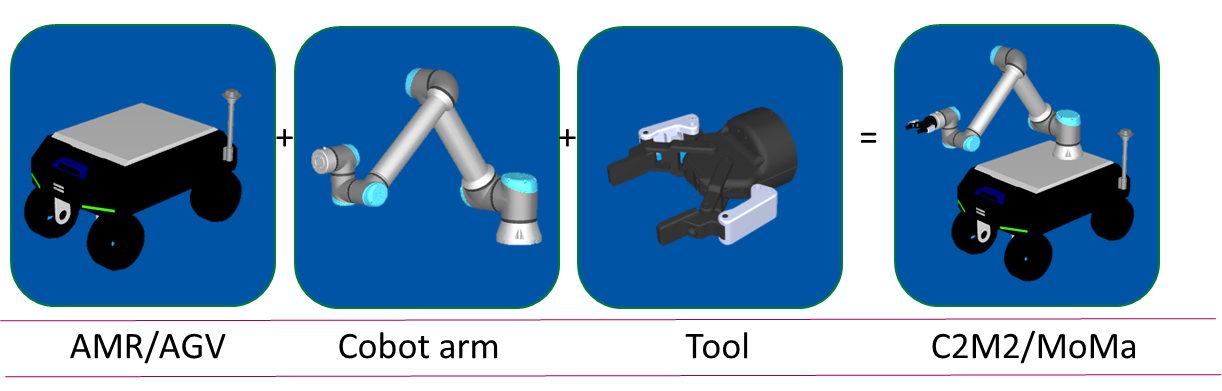
Figure 1: Constituent elements of a platform-mounted collaborative robot (or MoMa).
The main application of this device subject is to increase the level of factory automation in sectors where today automation has leave penetration, such as intralogistics and machine tending. In these scenarios, the robot can move raw materials, products in the manufacturing process or even search for machine replacement parts (such as a cutting head for a CNC). In any case, the MoMa will be able to perform the task either autonomously or as an assistant to a human operator (see figure below).

Figure 2: Factory scenario where a MoMa becomes one more resource of the factory where it can work alone or in collaboration with other human operators.
A likely scenario is that in the factory we will find more than one mobile robot, each of them with different capabilities and probably from different manufacturers. In this case it is important to have software that coordinates the tasks and distributes them appropriately according to the availability and/or capacity of each robot. Such software is known as a robot fleet manager.

Figure 3: A fleet manager coordinates the work of a set of robots.
There are many fleet management solutions on the market, but they are usually proprietary and compatible with only one brand of robot.
The goal of the final project of Degree is to deploy and test an open-source robotic fleet manager. The tests will be done both in simulation and with real robots.
As of essay of this document, it is planned to use open-rmf (Open-RMF: https://www.open-rmf.org/ ) or equivalent, see the following figure.
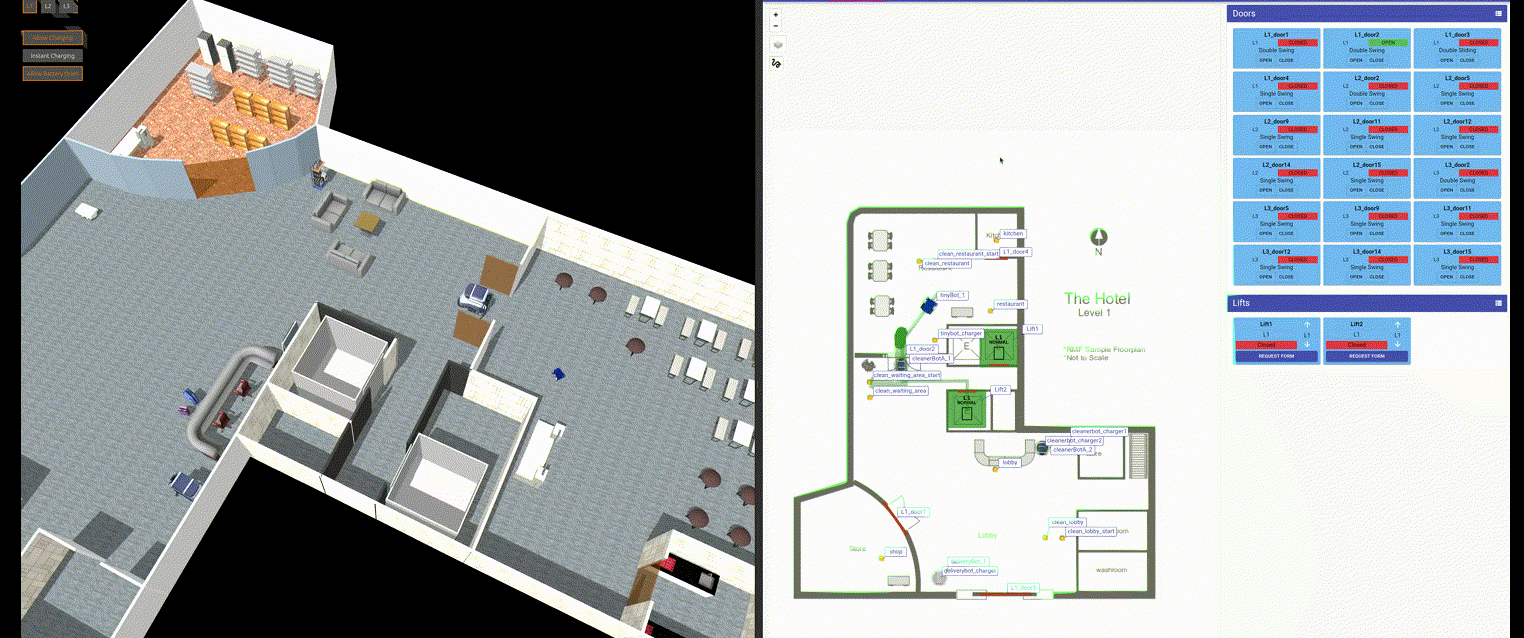
Figure 4: Screenshot of a simulation of coordinated fleets from open-rmf.
It is offered, during the execution of project:
-
Incorporation to the robotics group of researchers from the CEIT
-
Training in the software/hardware tools employed
-
Possibility of a job offer in a company in the sector.
Academic supervisor:
Ibon Elósegui
Tecnun. department for Electrical and Electronics Engineering
area thematic:
Electric drives, electric mobility.
Description and objectives:
In recent years, electrification is irreversibly reaching the automotive world. Although almost all manufacturers have adopted the radial motor with drive shaft option, the possibility of introducing in-wheel motors to avoid additional mechanical systems is gradually being analyzed.
The goal of project is to analyze the state of the art of existing in-wheel motors. From there, a complete design of the motor will be carried out from the electromagnetic and thermal point of view, using finite elements.

Academic supervisor:
Emilio Sánchez Tapia
Division CEIT:
Information and communications technologies. Intelligent Systems for Industry 4.0 Group. Vision and Robotics Subgroup
area thematic:
Robotics Engineering
Description and objectives:
Industry 4.0 has paved the way for multiple forms of automation that have as goal improve productivity and optimize work processes. In this context, the aim is to develop an intelligent mobile manipulator: a new robot subject that integrates the technology of an autonomous mobile robot and a highly efficient collaborative robotic arm capable of performing various operations.
The idea of project is to develop a robot that can move, detect and avoid obstacles, explore its environment to recognize objects through artificial vision and perform part handling tasks, being able to interact with operators. With the idea of implementing a digital transformation model , required today in real factory environments, robots, control elements, sensors and other onboard elements will be connected to each other through a digital platform to control the process in real time and from anywhere.
Currently CEIT has already developed a first working prototype (see figure below).
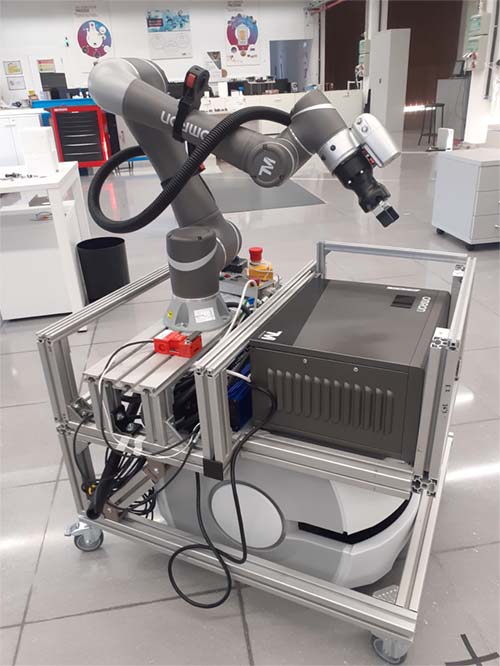

The task of this GFP would be the programming under ROS-2 of a sequence of tasks for the robot to interact with a classic robotic cell. The specific case to be developed will be for the robot to go to a archive of parts to be processed, bring them to the cell, wait for their processing and take them to another storeroom of already sorted parts.
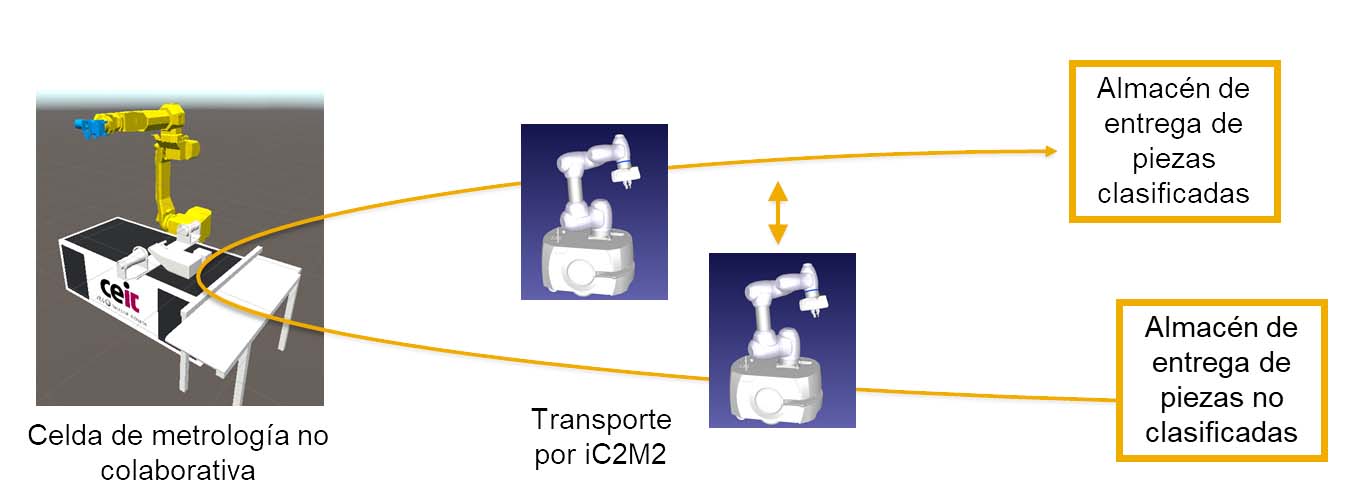
Under this simple task, the concepts of:
- Collaborative mobile robotics
- Machine tending
- Control in force
- Problem of synchronisation of two automatic devices
Programming skills in C/C++, Python or java-script are required.
Academic Supervisor: Miguel Martínez-Iturralde.
Division CEIT: Electric Vehicle and Smart Grids.
area subject: Electrical Engineering.
Description and objectives: In recent years there has been an exponential growth in aeronautical applications related to small electrically propelled vehicles: drones, flying taxis, vertical take-off vehicles (VTOLs), etc. In order to obtain electric flying vehicles with a practical range, it is essential that the weight of their components be kept to a minimum. In the case of electric motors, this means increasing the power density above the values of current solutions.
In this PFG we want to design a high power density motor for application in drones and small electric aircraft. The student will handle professional tools for the design and simulation of electrical components and will work in all the areas involved in developing a system: electromagnetic, thermal, mechanical, etc.

Academic Supervisor: Miguel Martínez-Iturralde.
Division CEIT: Electric Vehicle and Smart Grids.
area subject: Electrical Engineering.
Description and objectives: The development of hybrid and all-electric aeronautical applications is a reality, with numerous projects that have demonstrated on a small scale the feasibility of a quieter and more environmentally friendly aeronautics. In this sense, the major players in the electric sector (Airbus, Boeing, Rolls-Royce, etc.) are devoting great efforts to the electrification of commercial aircraft.
One of the challenges for the development of electrically powered aircraft is related to the design of high voltage electrical insulation systems that can operate at high altitudes, where air pressure is minimal and the risk of electrical discharges is higher. Currently, Ceit is involved in a European project to develop insulation systems that will be applicable in tomorrow's electric aircraft.
The task of this PFG would be to simulate aircraft electrical systems using commercial finite element software and obtain criteria from design for subsequent application to electric aircraft.

Academic Supervisor: framework Satrústegui.
Division CEIT: Electric Vehicle and Smart Grids.
area subject: Electrical Engineering.
Description and objectives: The noise generated by electric motors is becoming increasingly important due to the fact that it is embedded in systems where comfort is a very important aspect (e.g. electric cars). In this sense, this PFG tries to characterise the noise in an electric motor by performing a multiphysical analysis, starting by characterising the machine at an electromagnetic and thermal level and then developing a mechanical analysis that results in obtaining the noise generated at different levels of torque and rotational speed.

Academic Supervisor: Jesús Paredes.
Division CEIT: Electric Vehicle and Smart Grids.
area subject: Electrical Engineering.
Description and objectives: During the last decade, many of the aircraft auxiliary systems (pneumatic, hydraulic and mechanical) have been replaced by electric or hybrid actuators, due to incentives for the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and the reduction of operation and maintenance costs. This has led to a considerable increase in the electrical power installed in aircraft.
Traditionally, the turbines were started by a pneumatic system and the energy needed to power the aircraft's electrical systems was produced by generators coupled to the turbines. Today, the two systems have converged into a single electrical machine capable of working as both an engine and a generator. These systems include aircraft turbine starter/generators. The increasing demand for electrical energy and the limited space for starter/generators make it necessary to increase the power density of these machines.
The size, and therefore the weight and cost, of an electrical machine is primarily determined by the heat extraction and temperature limit of the materials used in its manufacture. Oil cooling systems have promising characteristics. Among all the oil cooling systems (spray, oil-dripping...), we intend to address in this project the oil-flooded stator systems.
The goal of this project is that the student are familiar with simulation tools fluid and cooling systems and to draw conclusions in order to optimize oil cooling systems for aircraft engines.
Academic Supervisor: Gurutz Artetxe.
Division CEIT: Electric Vehicle and Smart Grids.
area subject: Electrical Engineering.
Description and Objectives: Induction heating is an efficient and fast method of generating heat. It can be employee in various applications where tempering, brazing or melting of metals is required. CEIT is interested in developing computational tools (based on a set of previously developed tools) for use in the design of induction heating systems for formwork. The goal of this project is to model the electromagnetic and heating behavior of a formwork heating system and to perform optimization studies with them in order to carry out the design of a practical case.

- profile/Degree: Industrial Technologies, Mechanics, Electricity, Industrial Electronics.
- Academic Supervisor: Juan Carlos Ramos.
- department/area: department of Mechanical Engineering and Materials / area of Thermal and Fluid Engineering.
- Description: The aim is to solve by means of the Finite Difference Method a thermal model of the generation and conduction of heat in the core and coils inside a transformer. The equations of the model and the solution by the iterative Gauss-Seidel method will be implemented in Matlab. Heat transfer issues will be applied. For further information please contact the professor.
