Offers in: Industrial Electronics Engineering
Academic supervisor:
José Martín Echeverría Ormaechea
CEITTecnundepartment :
CEIT: Transportation and Energy Division
area :
Power Electronics, Piezoelectric Actuators, Nanometric Positioning
Description and Objectives:
Piezoelectric actuators used in high-precision positioning systems require power stages capable of supplying high voltages—typically between 100 V and 150 V—and transient currents associated with their predominantly capacitive nature. Although commercial controllers exist for this subject actuator, many have closed and limited configurations that make it difficult to optimize their performance or incorporate new specific functionalities.
The goal of project develop and validate a complete power electronics system that allows for the precise and safe excitation of piezoelectric actuators intended for positioning applications. The system must generate programmable control signals (unipolar or bipolar), operate over voltage ranges suitable for different types of actuators, and provide a dynamic response that allows for the evaluation of both the static and transient behavior of the device.
The power stage will include:
-
Implementation of voltage conversion stage to levels suitable for piezoelectric excitation (e.g., boost, flyback, or high-voltage linear power supply topologies).
-
amplification stage design capable of supplying reactive current and maintaining the linearity required for precision applications.
-
Implementation of control and modulation systems necessary to generate ramps, dynamic profiles, or sinusoidal test signals.
-
Internal sensing and monitoring of core topic parameters, such as applied voltage, instantaneous current, or system temperature.
This project students to delve deeper into the design high-voltage power converters, precision analog electronics, capacitive load control, and protection techniques, result fully functional and documented piezoelectric module .
Academic Supervisor:
Hector Solar
department Tecnun CEIT:
Tecnun: Electrical and Electronic Engineering department
subjectarea :
electronicdesign
Description and objectives: The goal of this project is the design of a mixer and its integration with a low noise amplifier (LNA), to develop the analog front-end (red box) of a semiconductor qubit reading system. Specifically, the electronics for electron spin qubits will be developed. The design tool is CADENCE, and the technology to be used is IHP SiGe BiCMOS 0.35um, as it has models for 4K temperatures. The student must perform the schematic design , optimize its performance, design the layout and integrate it with the LNA.
Academic Supervisor:
Ainhoa Galarza
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT: Transport and Energy Division
subjectarea :
Industrial Automation
Description and objectives:
Power converters for automotive applications typically communicate with the outside via buses such as CAN, serial port or Ethernet. The developer can send commands and receive information from a computer to diagnose the equipment, but with very rudimentary applications. The main purpose of the project is to develop a PC application to manage communications with the converter, and at the same time interact with the test bench devices (voltage sources, oscilloscopes, etc.).
The application must autonomously execute previously programmed tests by sending sequences of commands to all the elements of the bench; allow real-time data visualization by adjusting channels, scales and units; and export data to keep a secure record of all the activity, both of the converter operation and oscilloscope waveform captures at specific times of the essay. The essay sequences will be set up in a user-friendly way in the application environment, allowing to incorporate conditional logic to adapt the test flow to the conditions detected during the execution.
All actions, errors and results will be recorded in a log system, which will facilitate the audit and follow-up of the tests performed.
Academic Supervisor:
Isabel Ayerdi - Aitor Larrañaga Jaio
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT: Materials and Manufacturing Division: Precision Laser Manufacturing group.
subjectarea :
Industrial Automation, Optical Metrology, Profilometry, Materials Characterization, Quality Control, Data Science, Artificial Intelligence.
Description and Objectives:
Optimization and control of laser processes using AI models requires vast data sets linking entrance parameters (power, scan speed, frequency, pitch, etc.) to output quality metrics. The student will collaborate in the creation of a high precision micromachining database from samples etched with various laser conditions.
The main task of the student will be the development and standardization of a methodological automation tool that interacts with the Sensofar S Neox 3D profilometer to massively and repeatably characterize laser micromachining samples. The student will have to configure and implement the routines in the Sensofar software to automate the acquisition of 3D profilometry data and the subsequent processing for the extraction of core topic metrics (depth, roughness, angles, etc.).
This process will eliminate the need for manual measurements, creating a clean, structured and robust data stream that will feed a database for AI creation. If automation is achieved quickly, the project will include a basic AI implementation phase on the data generated in Python.
Objectives:
-
Standardize and document the acquisition protocol using the SensoSCAN MMR (Multiple Measurement Routine) for the automation of the XY stage and measurement sequence.
-
Develop and implement Analysis Recipes in SensoPRO for the automatic calculation and extraction of quality metrics (roughness, depth, wall angles) from the data obtained.
-
Create the data workflow that combines the process parametersentrance) with the quality metrics (output) in a structured dataset ready for Machine Learning.
If time permits, implement a simple Machine Learning algorithm to perform the first quality prediction on the generated dataset.
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcarcel Garcia / Cristina Rodriguez
department Tecnun CEITTecnun:
CEIT - ICT Division / PTM
subjectarea :
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science, Materials.
Description and Objectives:
development of a robust software application (preferably in Python) for parameter optimization of material constitutive equations (known models in the literature).
The goal is to automate the task of fitting models to experimental data (read from Excel/CSV) to predict mechanical properties. It is required to compare different optimization algorithms to determine the best fitting strategy. The project should be integrated or be the basis of an existing application.
Proposed Activities:
-
Literature review of constitutive models and optimization algorithms.
-
Mathematical formulation of the optimization problem (error function).
-
Implementation of data reading (Excel/CSV) and constitutive equations.
-
Implementation and comparison of at least two optimization algorithms (e.g., Levenberg-Marquardt vs. Genetic Algorithms).
-
development the Username interface for loading, adjustment and display of results.
-
Validation and analysis of the effectiveness of the software and algorithms applied.
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcárcel García
department Tecnun CEIT:
ICT Division
subjectarea :
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science
Description and Objectives:
development of a Python application to automate exploratory data analysis (EDA) and predictive regression modeling.
The goal is to build a tool able to read a database (CSV/SQL), automatically classify variables (numerical, categorical), perform univariate and bivariate statistical studies (correlations, graphs) and, finally, automatically apply and compare regression models for a variable of interest. The goal is to offer a robust software for the quick start of Data Science projects.
Proposed Activities:
-
Review of AutoEDA and AutoRegression techniques.
-
Intake module : Data reading and automatic classification of variables.
-
EDA module : Implementation of statistical studies and automatic graphs (univariate and relationship between variables).
-
Regression module : Automatic preprocessing and fitting/comparison of multiple regression algorithms (simplified AutoML).
Username interface: development of an interface (e.g., Shiny) for the visualization of results and insights.
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcárcel García
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT - ICT Division
area subject:
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science
Description and objectives:
The maintenance scheduling problem, known as the Maintenance Scheduling Problem or Maintenance Scheduling Problem, consists of organizing maintenance activities within a schedule in an optimal manner. This problem seeks to minimize interruptions and operating costs by ensuring that both preventive and corrective maintenance are performed at the appropriate times.
The goal of this final Degree project is to develop an optimization tool that addresses the efficient scheduling of maintenance schedules. The tool will be developed preferably in Python, with additional Matlab or R options.
Proposed activities for the student:
Bibliographic review of the most common optimization problems and algorithms applied in maintenance scheduling.
2. Mathematical formulation of the problem, establishing the relevant criteria and restrictions.
3. Implementation of the solution using a heuristic optimization algorithm or open source solvers.
4. Analysis of results and comparison of the effectiveness of the applied approach , with recommendations for its use in different maintenance situations.
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcárcel García
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT - ICT Division
area subject:
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science
Description and objectives:
The application of time-dependent covariates in survival analysis has improved the prediction of time to default in behavioral credit scoring models. However, when these covariates are endogenous, two problems occur: estimation bias and the lack of a framework to predict the future values of the event and the covariates.
Joint models are a statistical approach that simultaneously integrates longitudinal and survival data, allowing to model the joint evolution of an event of interest (such as time to default) and time-dependent endogenous covariates. This project explores for the first time the application of discrete-time joint models to credit scoring, and proposes a novel extension by including autoregressive terms in the endogenous covariates.
The project will apply these methods to U.S. mortgage data, evaluating whether discrete-time joint models improve predictive accuracy compared to traditional survival models and whether performance is optimized by including an autoregressive term.
Proposed activities for the student:
1. Literature review on joint models and their application in credit scoring.
2. Mathematical formulation of the joint model in discrete time.
3. Implementation of the model in R or Python.
4. Analysis of results, comparing predictive performance against other models.
This project will allow the student to explore advanced statistical modeling techniques applied to financial data and improve predictions in the context of credit risk.
Academic Supervisor:
Dr. Carlos Alejandro Peñuelas Angulo
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT - ICT Division
subjectarea :
Information security, data analysis
Description and objectives:
The overall purpose of this project is the design and implementation of an architecture that offers data analysis functions (Machine Learning, data mining, etc.) as a service implementing mechanisms for the preservation of data privacy, also known as Privacy Enhancing Technologies (PETs). This can include from the use of advanced cryptographic mechanisms to federated learning.
The activities expected to be carried out during the execution of this project are:
-
Analyze examples of PETs applied to data analysis.
-
Design an architecture for privacy-preserving data analysis as a service.
-
Implement the architecture using state-of-the-art technologies.
Academic Supervisor:
Saioa Arrizabalaga
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT - ICT Division. data analysis and Information Management Group
area thematic:
Industrial process modeling. Cybersecurity.
Description and objectives:
Hybrid testbeds allow the study of offensive and defensive cybersecurity mechanisms in industrial environments and also their impact on the process under attack or to be defended.
This project would be focused on the generation of digital twins for industrial systems (e.g. wind turbines, water distribution networks...), based on existing Simulink models. The student will have to map sensors/actuators on the models, define operating states (normal, abnormal) to improve testbed monitoring and response capabilities, analyze potential system cybersecurity threats and develop mitigation strategies. Simulink models will be modified so that they can be integrated into the virtualized testbed so that they can be operated in real time.
Academic Supervisor:
Javier Cejudo
department CEITTecnun:
CEIT - ICT Division
subjectarea :
Coding and firmware, IoT, electronic design , embedded systems, wireless communications, industrial automation, security.
Description and objectives:
Remote FPGA programming from a microcontroller, without the need to use a specific programmer. The main goal is to implement the necessary logic in an embedded system subject microcontroller to act as FPGA programmer. The necessary wireless communications (Bluetooth, 4G...) must also be implemented to be able to perform this programming remotely and be accessible from anywhere in the world.
It is a project that proposes to work on physical elements in order to test and promote applied practical skills.
Academic Supervisor:
Iñigo Adin
department CEITTecnun:
CEIT - ICT Division
subjectarea :
Intelligent surfaces, Wireless communications, Electromagnetic simulation, State of the art, Defense, Security, Selective concealment, Electronic design .
Description and objectives:
Embark on a pioneering Final Project exploring the future of communications and defense through programmable wireless environments. This project dives into the technologies that are redefining the interaction with electromagnetic waves, such as Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS), metamaterials and the emerging Multifunctional RIS (MF-RIS) that integrates sensing capabilities for autonomous operation. Your mission statement will be to perform a comprehensive state-of-the-art review, analyzing the fundamental techniques and trends presented in the sources, from passive beamforming and channel optimization to challenges in wideband channels and near-field phenomena. From this research, you will be expected to propose innovative applications that leverage these capabilities not only to revolutionize 6G communications, improving coverage, security and efficiency, but also to develop cutting-edge defense systems, including secure tactical communications, stealth technologies to reduce radar and acoustic detectability, and new forms of electronic warfare and environmental surveillance.
Academic Supervisor:
Dr. Emilio Sánchez Tapia
department CEITTecnun:
CEIT - Vision and Robotics
subjectarea :
Industrial automation/robotics
Description and objectives:
This Degree final project is born as a direct continuation of a previous work in which the same unscrewing operation was successfully automated. In that first phase, the control architecture was based on a traditional industrial system, using a PLC to govern the KUKA robot. Having validated the mechanical and vision feasibility of the system, this new project focuses on exploring an alternative and more flexible control architecture.
The new goal is therefore to approach the control from two different perspectives in order to compare its performance. Instead of using the PLC, a specialized controller, extremely reliable and designed to operate in real time, the same process will be implemented using ROS (Robot Operating System) on a conventional computer. ROS is not an operating system like Windows, but a set of open source software tools that greatly facilitates the programming of robots and the integration of components such as cameras or artificial intelligence algorithms. The final scope is to evaluate and quantify the advantages and disadvantages of each approach: the robustness and determinism of the industrial PLC versus the flexibility, speed of development and processing power offered by a system based on ROS and a PC.
Tasks to be performed by the student:
-
Familiarization with previous work
-
Learning the programming technique of the Kuka Issy robot.
-
Learning to use the ROS operating system
-
Programming from ROS of the execution of a sequence of paths for screwing/unscrewing (language to be defined, it can be in Python or C++).
-
Testing and evaluation of the performance achieved
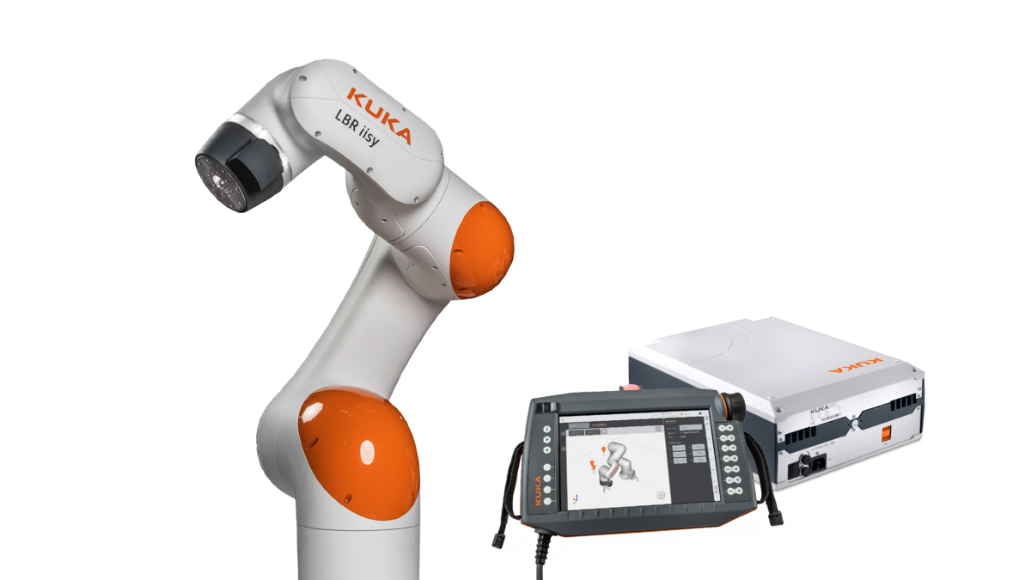

Photo of the KUKA collaborative robot to be used in the PFG.
- Academic supervisor:
Adam Podhorski
area thematic:
design electronic
Description and objectives:
This project is part of a larger research project whose purpose is to measure environmental noise from one or more drones. The main goal of the proposed GFP is to design and implement the electronic platform necessary for the operation of an acoustic camera mounted on a drone.
An acoustic camera is a device that measures the noise level from different directions and represents it in a heat map superimposed on a real image. Its application is especially useful in noise pollution studies, noise source localization and diagnostics in industrial environments. Here is an example of this subject of technology: GFaI acoustic camera.
What does the project consist of?
- Design and build a microphone array with an integrated camera.
- Capture signals with PDM microphones (microphones with digital output).
- Integrate the system in a drone and perform test flights in the sports center with real noise sources.
The focus of the PFG will be on the design, implementation and validation of the electronic system, not so much on signal processing.
Academic Supervisor:
Saioa Arrizabalaga
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
ICT Division. Group of data analysis and Information Management
area thematic:
Industrial process modeling. Cybersecurity.
Description and objectives:
Hybrid testbeds allow the study of offensive and defensive cybersecurity mechanisms in industrial environments and also their impact on the process under attack or to be defended.
This project would be focused on the generation of digital twins for industrial systems (e.g. wind turbines, water distribution networks...), using existing Simulink models. The student will have to map sensors/actuators on the models, define operating states (normal, abnormal) to improve testbed monitoring and response capabilities, analyze potential system cybersecurity threats and develop mitigation strategies. Simulink models will be modified so that they can be integrated into the virtualized testbed so that they can be operated in real time.
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcárcel García
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
ICT Division. Group of data analysis and Information Management
area subject:
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science
Description and objectives:
The application of time-dependent covariates in survival analysis has improved the prediction of time to default in behavioral credit scoring models. However, when these covariates are endogenous, two problems occur: estimation bias and the lack of a framework to predict the future values of the event and the covariates.
Joint models are a statistical approach that simultaneously integrates longitudinal and survival data, allowing to model the joint evolution of an event of interest (such as time to default) and endogenous time-dependent covariates. This project explores for the first time the application of discrete-time joint models to credit scoring, and proposes a novel extension by including autoregressive terms in the endogenous covariates.
The project will apply these methods to U.S. mortgage data, evaluating whether discrete-time joint models improve predictive accuracy compared to traditional survival models and whether performance is optimized by including an autoregressive term.
Proposed student activities:
-
Literature review on conjoint models and their application in credit scoring.
-
Mathematical formulation of the model set in discrete time.
-
Implementation of model in R or Python.
-
Analysis of results, comparing predictive performance against other models.
This project will allow the student to explore advanced statistical modeling techniques applied to financial data and improve predictions in the context of credit risk.
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcárcel García
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
ICT Division. Group of data analysis and Information Management
area subject:
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science
Description and objectives:
The maintenance scheduling problem, known as the Maintenance Scheduling Problem, consists of optimally organizing maintenance activities within a schedule. This problem seeks to minimize interruptions and operating costs, ensuring that both preventive and corrective maintenance are performed at the right times.
The goal of this end of Degree project is to develop an optimization tool that addresses efficient scheduling of maintenance schedules. The tool will be developed preferably in Python, with additional Matlab or R options.
Proposed student activities:
-
Bibliographic review of the most common optimization problems and algorithms applied in maintenance scheduling.
-
Mathematical formulation of the problem, establishing the relevant criteria and restrictions.
-
Implementation of the solution using a heuristic optimization algorithm or open source solvers.
-
Analysis of results and comparison of the effectiveness of the applied approach , with recommendations for its use in different maintenance situations.
Academic Supervisor:
Markos Losada
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
Transport and Energy Division: Transport and Sustainable Mobility Group.
area subject:
design electronic, coding, data processing
Description and objectives:
The approach of this final work of Degree focuses on the analysis of advanced distance estimation technologies that could be integrated into a system for a wristband to analyze the game of Padel. The project is divided into several phases, starting with a comprehensive analysis of existing commercial systems, evaluating their advantages and proposing improvements. The review of current technologies such as time-of-flight (ToF), Lidar and ultrasound sensors is fundamental to select the most appropriate technology for this purpose. The proposal for improvement will include technology selection, the development of a specific algorithm and system integration, considering factors such as size, cost and power consumption. The goal is for the student to not only gain knowledge about these technologies, but also to propose a concrete solution that can be implemented.
In the implementation phase, the student will be responsible for integrating the selected sensors and developing a system capable of detecting a matrix of points to accurately estimate distances. The results obtained will be analyzed to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm and determine the feasibility of its implementation in a commercial product. This project not only seeks to improve the paddle tennis playing experience, but also to explore potential applications of these technologies in other fields, such as weighing or wagon monitoring.
Academic Supervisor:
Iñigo Adín
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
Transport and Energy Division: Transport and Sustainable Mobility Group.
area subject:
Artificial intelligence learning, coding, data processing.
Description and objectives:
This final work of Degree has as main goal the development and the implementation of machine learning models in low power microcontrollers, specifically of the STM32 family, using TensorFlow Lite. The project focuses on the application of these models in the transportation sector, with a particular approach on the analysis and improvement of automatic braking systems.
To achieve this goal, the student should:
Training in Tools and Technologies:
Acquire knowledge of TensorFlow Lite for microcontrollers, through Machine Learning resources such as Andrew Ng's documentation, and "Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras and TensorFlow", as a foundation and using Wes McKinney's "Python for the data analysis" as reference letter for management and data analysis.
development of Machine Learning Models:
Design and train machine learning models that can be optimized for execution on low-power microcontrollers.
Evaluate the performance of these models in terms of accuracy, efficiency and energy consumption. For this purpose, data will be collected with a sensorized brake bench and the models will be trained with them.
Integration in Microcontrollers:
Implement the developed models on STM32 microcontrollers using TensorFlow Lite. Ensure that the integration is efficient in terms of resources and reliability of the results.
Application in the Transportation Sector:
Apply integrated models to improve the automatic braking function in vehicles, analyzing real-time data to optimize system safety and efficiency.
Evaluate the impact of the implementation in test scenarios, adjusting the models as needed to improve performance.
The documentation and results will be organized documenting the references and the process of development. The results obtained will be presented, highlighting the improvements achieved in the automatic braking function and possible future applications of the developed technology.
Academic Supervisor:
Ainhoa Cortés/Juan Manuel Galán
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
Materials and Manufacturing Division : Intelligent Systems for Industrial 4.0 Group.
area subject:
design electronics, embedded systems
Description and Objectives:
The goal of this PFG is to take contact from student with the RISC-V architecture, its features and its use in embedded systems. For this purpose, a comparison of (at least) a commercial RISC-V based microcontroller against RISC-V CEIT, a RISC-V microcontroller developed at CEIT. This work will attempt to identify differences in various aspects such as (but not limited to):
- Functionality (ISA Extensions, Peripherals, Pinout...)
- Frequency of work
- Consumption (taking into account the available working modes)
- Tools for development
In addition, the student should propose improvements to the design microcontroller developed in-house to improve the deficits revealed from the above comparison.
Academic Supervisor:
Andoni Irizar/Juan Manuel Galán.
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
Materials and Manufacturing Division : Intelligent Systems for Industrial 4.0 Group.
area subject:
design electronics, embedded systems
Description and objectives:
Within one of the research lines of CEIT, a RISC-V based microcontroller has been developed currently available for Xilinx and Microchip FPGAs. The main goal of this PFG is the adaptation of this microcontroller to FPGA Altera by means of:
-
Analysis of Altera FPGA features
-
Identification of the microcontroller elements to be adapted (parameters, macros...)
-
development of simulation scripts and functional verification
-
development of synthesis scripts and constraints (timing and pinout)
-
Synthesis and plate verification
Academic Supervisor:
Juan Manuel Galán/Andoni Irizar.
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
Materials and Manufacturing Division : Intelligent Systems for Industrial 4.0 Group.
area thematic:
Embedded systems
Description and objectives:
Within one of the research lines of CEIT, a RISC-V based microcontroller (RISC-V CEIT) has been developed. The main goal of this PFG is the development of a bootloader for this microcontroller. Some of the activities to be performed are:
-
development and verification bookshop SW (in C) for access to report Flash.
-
development bootloader capable of loading SW via UART and SPI (among other functions)
-
Gap analysis development U-boot for RISC-V CEIT
Academic Supervisor:
Emilio Sanchez Tapia
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
Materials and Manufacturing Division: Robotics and Industrial Control Group.
area thematic:
Robotic Engineering
Description and objectives:
In the context of robotics in the 21st century, the concept of the connected factory arises where machines, mobile robots and humans coexist. Mobile robots may or may not include a robotic manipulator arm or MoMa (MObile MAnipulator). If there is only the mobile robot, it is usually referred to as AMR (Autonomous Mobile Robot) or AGV (Autonomous Guide Vehicle) according to its Degree of freedom in navigation (see figure below).
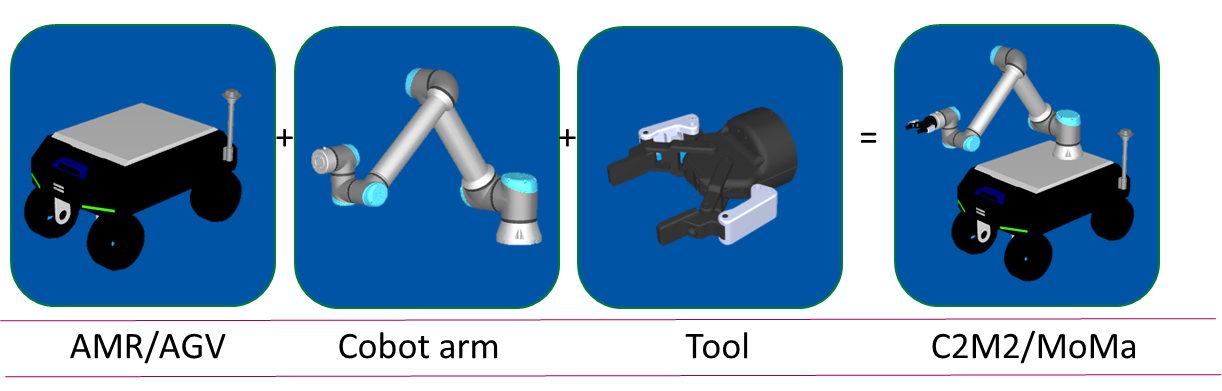
Figure 1: Constituent elements of a platform-mounted collaborative robot (or MoMa).
The main application of this device subject is to increase the level of factory automation in sectors where today automation has leave penetration, such as intralogistics and machine tending. In these scenarios, the robot can move raw materials, products in the manufacturing process or even search for machine replacement parts (such as a cutting head for a CNC). In any case, the MoMa will be able to perform the task either autonomously or as an assistant to a human operator (see figure below).

Figure 2: Factory scenario where a MoMa becomes one more resource of the factory where it can work alone or in collaboration with other human operators.
A likely scenario is that in the factory we will find more than one mobile robot, each of them with different capabilities and probably from different manufacturers. In this case it is important to have software that coordinates the tasks and distributes them appropriately according to the availability and/or capacity of each robot. Such software is known as a robot fleet manager.

Figure 3: A fleet manager coordinates the work of a set of robots.
There are many fleet management solutions on the market, but they are usually proprietary and compatible with only one brand of robot.
The goal of the final project of Degree is to deploy and test an open-source robotic fleet manager. The tests will be done both in simulation and with real robots.
As of essay of this document, it is planned to use open-rmf (Open-RMF: https://www.open-rmf.org/ ) or equivalent, see the following figure.
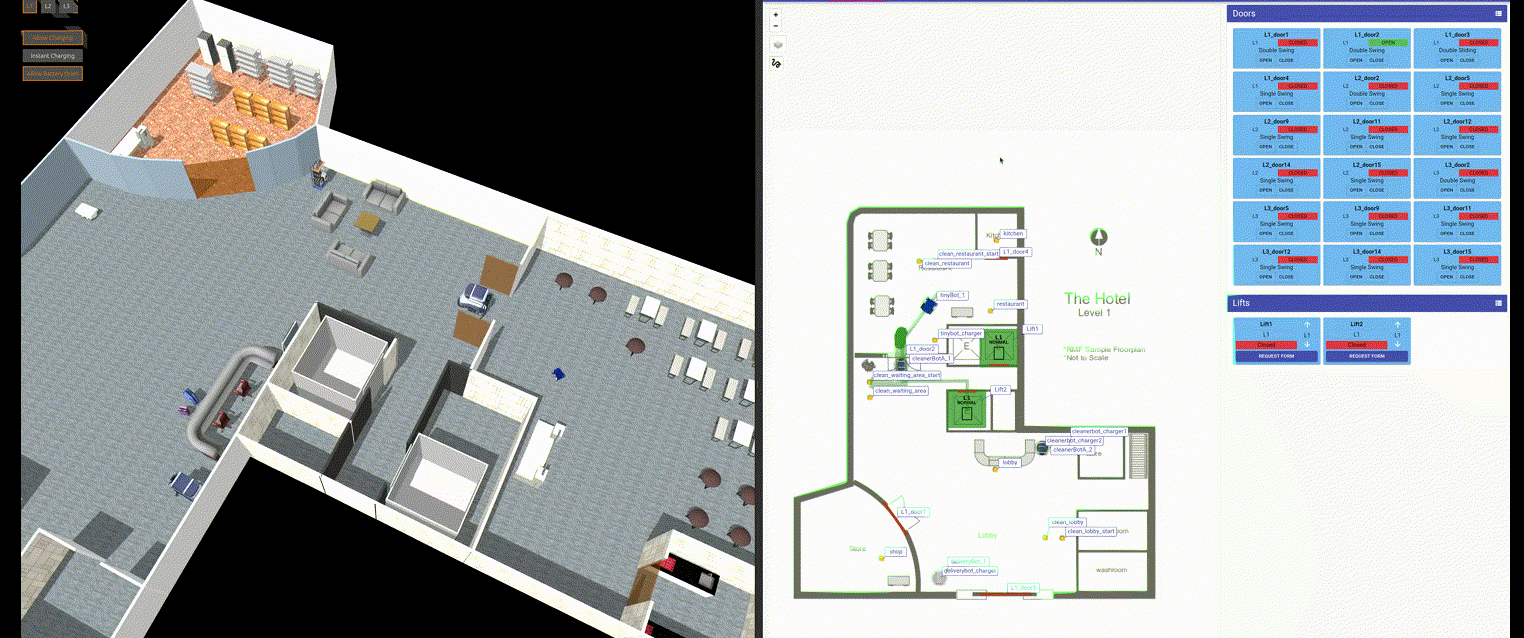
Figure 4: Screenshot of a simulation of coordinated fleets from open-rmf.
It is offered, during the execution of project:
-
Incorporation to the robotics group of researchers from the CEIT
-
Training in the software/hardware tools employed
-
Possibility of a job offer in a company in the sector.
Academic Supervisor:
Enrique Castaño Carmona
Division CEIT:
Advance Powder Metallurgy and Laser Manufacturing Group
area thematic:
Computing, modeling and simulation
Description and objectives:
The machining of materials using ultra-short pulse lasers is a very recent technology development and opens multiple possibilities in the field of functional surfaces, such as low friction coefficient surfaces in wind turbines or anti-icing surfaces in aeronautics.
Currently, Ceit is leading a European project in which one of its objectives is to develop a simulation software for the machining process with this subject of lasers. The mathematical modeling of the process is already well advanced, as well as its numerical implementation.
The task of this PFG will be to design and develop the graphical interface with the Username of the simulation program so that its use is easy and intuitive. The student will apply and extend his knowledge of Python programming, GUI (Graphic User Interface) and design UX/UI (User Experience/User Interface) to achieve an interface that allows Username an attractive experience of the simulation program.
Academic Supervisor:
Yuemin Ding
department Tecnun:
Electrical and Electronic Engineering
area thematic:
Telecommunication
Description and objectives:
Online monitoring and data collection in ultra-remote areas is specifically meaningful to investigate the local characteristics of climate change, biodiversity evolution, etc. It is also very important to prevent huge disasters, such as wildfires. However, online monitoring and data collection in ultra-remote areas have been challenging during the past decades. A major challenge is the lack of digital infrastructure for communication and data collection. However, the emerging satellite networking (such as Starlink) and low-power and long-distance IoT (such as MIoTy) technologies enable an alternate solution for online monitoring and data collection. The aim of this project is to develop a system based on satellite networks and low-power and long-distance IoT to enable online monitoring and data collection in ultra-remote areas.
Academic supervisor:
Ainara Rodríguez - Isabel Ayerdi
Division CEIT:
Materials and Manufacturing. Advanced Manufacturing in Powder Metallurgy and Laser Group.
Description and objectives:
Laser functionalization of surfaces is an approach widely used in a wide variety of applications and sectors, as it allows to provide final products with added functionalities, including, among others, decorative effects, the ability to repel liquids or improve the adhesion of coatings. At the moment Ceit is developing an international project of research and development in this last field, whose goal is to improve the adhesion of antibacterial and antiviral coatings to high traffic objects such as handles, switches or push buttons.
In the framework of this project in cooperation, a TFG is proposed whose goal is the design and implementation of a test bench for the characterization of the surface properties of the manufactured samples, among which are the improvement of adhesion, hydrophobicity/hydrophilicity characteristics or optical properties among others. In addition to the above, it will be necessary to implement an intelligent processing system for the data obtained by the measuring elements.
Academic supervisor:
Yago Olaizola
Division CEIT:
Materials and Manufacturing. Advanced Manufacturing in Powder Metallurgy and Laser Group.
Description and objectives:
Transparent materials are currently used in a multitude of applications in which their optical properties are particularly relevant: lenses, devices for optical communications, smart glasses or optical sensors, among others. In this context, the characterization of the optical properties is a point core topic in the development of the devices.
The goal of this project will be to design and implement an optical microscopy system, starting from different optical and mechanical elements, for the analysis of certain properties of transparent materials. After the validation of the equipment, we will proceed to study the optical behavior of this substrate subject after different laser engraving processes. In parallel, it will be necessary to implement an intelligent processing system for the data obtained by the measurement devices.
Academic supervisor:
Gemma García Mandayo
Division CEIT:
Materials and Manufacturing. Advanced Manufacturing in Powder Metallurgy and Laser Group.
Description and objectives:
The project is framed within the development of an innovative system for the measurement of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and coagulation, for application in clinical diagnostics. The main purpose of the system is to provide results of ESR and/or blood coagulation in a minimum time, with a minimum amount of sample and using sustainable materials, offering significantly higher performance than the devices currently available in the market, and thus allowing a faster and earlier diagnosis of pathologies such as infections, tumors or autoimmune diseases.
The goal of project is the optimization of the sample characterization processes, developing a test bench and performing tests to improve the performance of the device.
Academic supervisor:
Íñigo Adín
Division CEIT:
ICT
area thematic:
NDT, RF, Transport
Description and objectives:
This project aims to design a system for detecting cracks in railway rails. At the level of the basic principle of detection, it is proposed here to be carried out by means of a radar technique in radio frequency technologies with the capacity to illuminate the rail in movement. The reflections received must be processed to determine the presence of cracks smaller than the size specified in the regulations before grinding the rail. With this project, the aim is to advance in the specification of the basic principle of detection, and to investigate the needs for mounting on a moving element.
Academic supervisor:
Íñigo Adín
Division CEIT:
ICT
area thematic:
IoT, Energy Harvesting, low energy consumption
Description and objectives:
This project proposes the acquisition and implementation of novel platforms for the transformation of motion, radio frequency, sound or wind into energy usable by autonomous IoT systems. There are currently more integrated and more efficient platforms that promise to provide power to electronic data collection and remote connection systems and it is important to know the real scope of their possibilities. This refers here to testing and merging the possibilities of taking advantage of unusual physical elements/events for these applications, to replace the usual solar panels.
Academic supervisor:
Leticia Zamora Cadenas - Iker Aguinaga Hoyos.
Division CEIT:
Information and Communication Technologies. Intelligent Systems for Industry 4.0 Group.
area thematic:
Telecommunication/Industrial Engineering
Description and objectives:
Indoor location systems are a booming element in recent years. Whether using radiofrequency technologies, inertial sensors or artificial vision systems, the location of objects or people in interior spaces is an element core topic in many applications (tracking of parts, access to security areas, tracking of people, augmented reality, etc.).
To determine and evaluate the accuracy of a location system, the most common method is to measure guide a number of control points or tests in a controlled environment to determine the accuracy of the system. However, this subject measurement is always subject to measurement errors, human error, and the impossibility of tracking a moving element in real time. Another widespread option, especially when the accuracy is to be evaluated dynamically, is to resort to cost-effective systems that allow the creation of the real path or "ground truth", such as, for example, vision tracking systems. However, it is not always possible to deploy this type of system subject , or the economic means to do so are not always available. Therefore, being able to evaluate the accuracy of indoor positioning systems at a low cost is still a problem that researchers and companies are trying to solve.
Currently Ceit has a line of research associated with positioning systems for indoor spaces, in which it works with various companies to provide solutions to their needs. This is why the need for a ground truth system that is easy to install and not too expensive was born.
The task of this GFP would be to develop a ground truth system, using virtual/augmented reality systems, for subsequent use in evaluating the accuracy of the proprietary indoor location system Ceit. HTC Vice, Oculus Quest and Hololens 2 hardware are available for the development of this system using the Unity3D programming platform. The candidate must have programming skills in C# or similar languages such as C++ or Java.
Academic supervisor:
Emilio Sánchez Tapia
Division CEIT:
Information and communications technologies. Intelligent Systems for Industry 4.0 Group. Vision and Robotics Subgroup
area thematic:
Robotics Engineering
Description and objectives:
Industry 4.0 has paved the way for multiple forms of automation that have as goal improve productivity and optimize work processes. In this context, the aim is to develop an intelligent mobile manipulator: a new robot subject that integrates the technology of an autonomous mobile robot and a highly efficient collaborative robotic arm capable of performing various operations.
The idea of project is to develop a robot that can move, detect and avoid obstacles, explore its environment to recognize objects through artificial vision and perform part handling tasks, being able to interact with operators. With the idea of implementing a digital transformation model , required today in real factory environments, robots, control elements, sensors and other onboard elements will be connected to each other through a digital platform to control the process in real time and from anywhere.
Currently CEIT has already developed a first working prototype (see figure below).
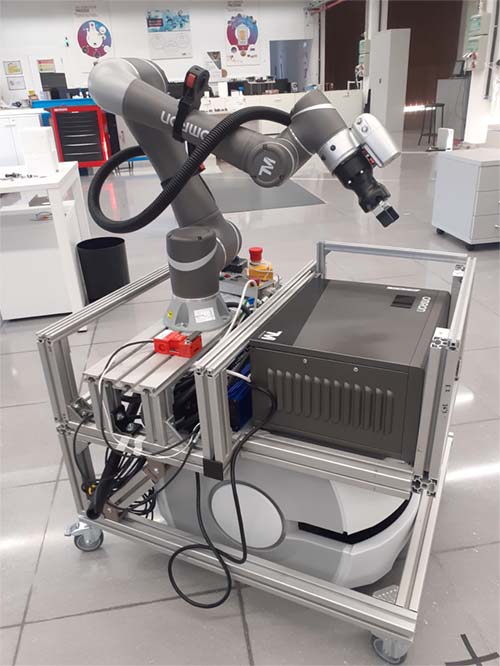

The task of this GFP would be the programming under ROS-2 of a sequence of tasks for the robot to interact with a classic robotic cell. The specific case to be developed will be for the robot to go to a archive of parts to be processed, bring them to the cell, wait for their processing and take them to another storeroom of already sorted parts.
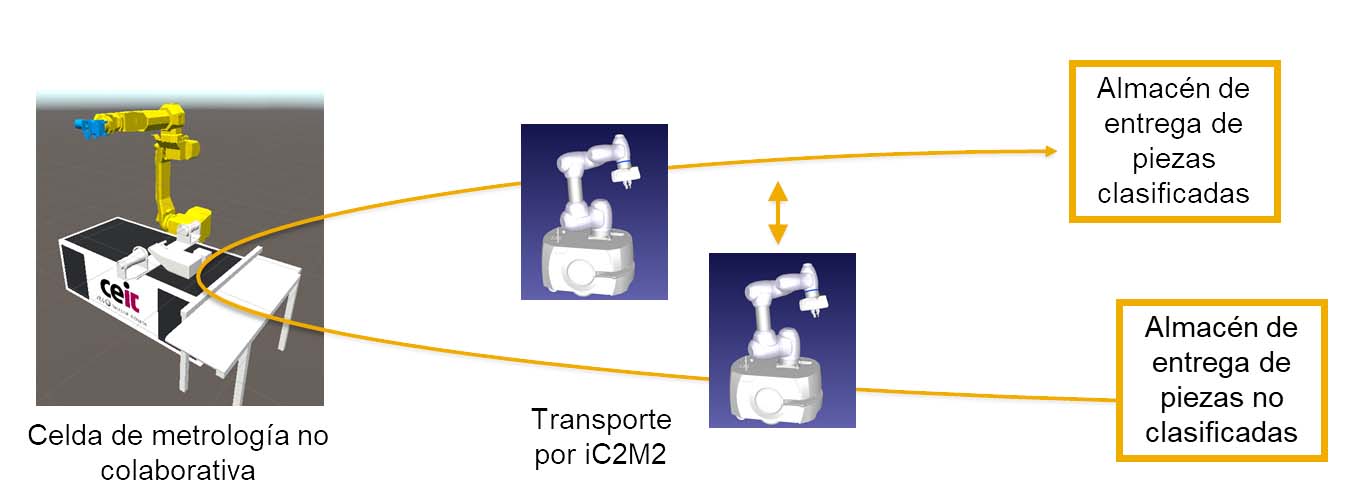
Under this simple task, the concepts of:
- Collaborative mobile robotics
- Machine tending
- Control in force
- Problem of synchronisation of two automatic devices
Programming skills in C/C++, Python or java-script are required.
Academic Supervisor: Gurutz Artetxe.
Division CEIT: Electric Vehicle and Smart Grids.
area subject: Electrical Engineering.
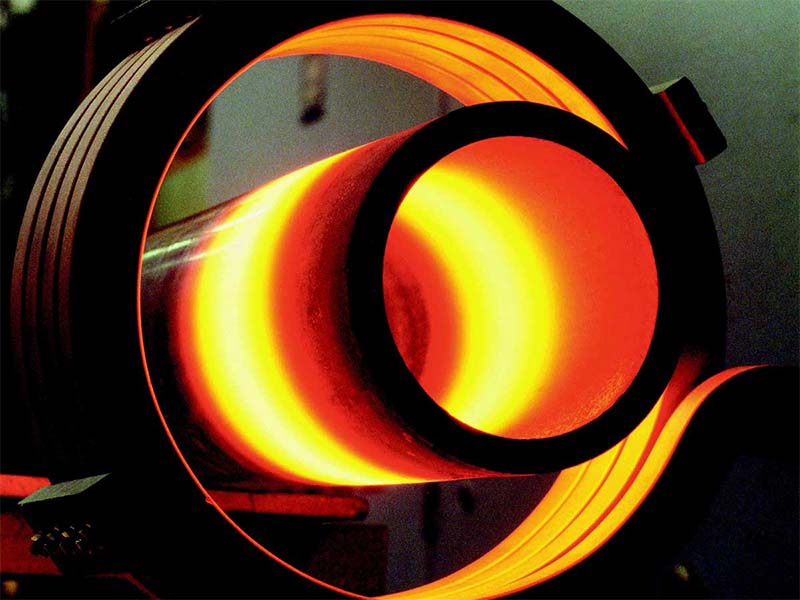
Description and Objectives: Induction heating is an efficient and fast method of generating heat. It can be employee in various applications where tempering, brazing or melting of metals is required. CEIT is interested in developing computational tools (based on a set of previously developed tools) for use in the design of induction heating systems for formwork. The goal of this project is to model the electromagnetic and heating behavior of a formwork heating system and to perform optimization studies with them in order to carry out the design of a practical case.

- profile/Degree: Industrial Technologies, Mechanics, Electricity, Industrial Electronics.
- Academic Supervisor: Juan Carlos Ramos.
- department/area: department of Mechanical Engineering and Materials / area of Thermal and Fluid Engineering.
- Description: The aim is to solve by means of the Finite Difference Method a thermal model of the generation and conduction of heat in the core and coils inside a transformer. The equations of the model and the solution by the iterative Gauss-Seidel method will be implemented in Matlab. Heat transfer issues will be applied. For further information please contact the professor.
Academic supervisor:
Andoni Irizar
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
CEIT. Materials and Manufacturing Division
area thematic:
Electronic systems
Description and objectives:
In today's industrial processes it is increasingly necessary to monitor the manufacturing process and the quality of the components resulting from the process. There are a wide variety of methods that allow such monitoring in real time, that do not require separating the parts from the rest for analysis and that do not damage the parts in the process. The most commonly used inspection techniques are those using electromagnetic fields, ultrasonic signals and machine vision. This project deals with ultrasonic techniques. The Ceit has its own ultrasonic signal test bench that allows to generate and capture ultrasonic signals in a simple way from a PC. The goal of project will consist of making a proposal of design of a miniaturized test bench (for example, the size of a Raspberry). As a comparison, the current design occupies the size of a Desktop computer. It would involve making a block diagram of the system, making a selection of components including the processing platform to be used and the components of the power source . Finally, it will be necessary to estimate the consumption and cost of the final equipment.
Academic supervisor:
Jorge Juan Gil.
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
CEIT. Intelligent Systems for Industry 4.0 Group.
area thematic:
Systems and Control Engineering
Description and objectives:
So far the control concepts are shown on the blackboard, by means of simulations or with videos. For the Control Engineering subject we want to build a mechanical control system (two pendulums coupled with springs) to be used for teaching purposes: to show in class the different behavior of the system before several controllers. To ensure portability, the system will be controllable through USB by means of an ARDUINO card . In a previous project the mechanical system has been built. In the proposed project several controllers will be programmed in C, in particular, a proportional-integral (PI) controller that allows "teleoperation" (that the Username moves one of the pendulums and the other one follows its movement without error in permanent regime).
