Offers in: Telecommunication Systems Engineering
Academic Supervisor:
Hector Solar
department Tecnun CEIT:
Tecnun: Electrical and Electronic Engineering department
subjectarea :
electronicdesign
Description and objectives: The goal of this project is the design of a mixer and its integration with a low noise amplifier (LNA), to develop the analog front-end (red box) of a semiconductor qubit reading system. Specifically, the electronics for electron spin qubits will be developed. The design tool is CADENCE, and the technology to be used is IHP SiGe BiCMOS 0.35um, as it has models for 4K temperatures. The student must perform the schematic design , optimize its performance, design the layout and integrate it with the LNA.
Academic Supervisor:
Hector Solar
department Tecnun CEIT:
Tecnun: Electrical and Electronic Engineering department
subjectarea :
Communications systems
Description and objectives: The goal of this project is to integrate a set of software and hardware tools to implement an audiovisual production center based on a semi-professional ATEM mixer.
The student will have to learn to use and integrate different audiovisual equipment: cameras, microphones, converters, mixers, cabling, computers, etc.; with software applications for remote control and operation of the center.
Academic Supervisor:
Santiago Miguel Olaizola / Iñigo Ramón Conde / Aitor Larrañaga Jaio.
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT: Materials and Manufacturing Division: Precision Laser Manufacturing group.
subjectarea :
Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Process Sensorization, Data Processing, Industrial Automation, Optical Metrology, Profilometry, Advanced Laser Processing, Materials Characterization.
Description and objectives:
This Final Degree project (PFG) addresses the growing need in Industry 4.0 to control and optimize advanced manufacturing processes. It focuses on the femtosecond laser as a versatile tool for materials processing (including ablation micromachining, surface and/or functional texturing, and controlled surface thermalization).
The project aims to create a Hybrid Intelligent Laser System that integrates predictivemodel (AI) with real-time monitoring data (sensing) to achieve on-line quality control and dynamic process optimization, independent of the specific processing application. The approach allows the developed methodology to be adaptable to multiple ultrashort pulse laser applications.
The objectives of this PFG are as follows:
-
Process Modeling and Digital Twin development (AI): Develop and evaluate Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning models (e.g., recurrent or convolutional neural networks) capable of acting as a digital twin of the process. The model shall predict a variety of result metrics (e.g., ablation depth, roughness, compositional changes or reflectivity) from the laser entrance parameters (power, scan speed, frequency, etc.).
-
Sensor Data Integration: Conceptualize and design the integration of entrance features from process monitoring systems (e.g., high speed cameras, pyrometers, plasma emission spectroscopy, or in-situ optical metrology). This is intended to enrich the database and allow the AI model to characterize the state of the ongoing process, not just the final results.
Participation in this PFG will allow the student to acquire a set of multidisciplinary skills and high demand in Industry 4.0, such as application of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning to advanced manufacturing problems; or integration and processing of large volumes of industrial sensorization and metrology data. Additionally, it will also allow the development of transversal core topic skills in the design of experiments, complex problem solving and critical analysis.
Academic Supervisor:
Ainara Rodriguez / Iñigo Ramón Conde / Aitor Larrañaga Jaio.
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT: Materials and Manufacturing Division: Precision Laser Manufacturing group.
subjectarea :
Data Processing, Industrial Automation, Optical Metrology, Profilometry Materials Characterization, Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Laser Micromachining.
Description and objectives:
This Final Degree project focuses on the application of advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) techniques to address the multi-objective optimization of a highly relevant manufacturing process: ultrashort pulse laser cold ablation.
The project starts from a pre-existing and characterizeddatabase , which contains the laser control parameters (power, scan speed, distance between passes, pulse train, etc.) as entrance features, and the quality metrics(depth and roughness) as output targets. It should be noted that the database is extensible, being able to incorporate new features or additional quality metrics to enrich the model and increase its predictive capacity.
The project pursues a double goal:
-
Process prediction: develop and evaluate neural regression models and other advanced ML approaches in order to build a digital twin of the process. Such a model will allow highly accurate prediction of the resulting depth and roughness from any combination of entrance parameters.
-
Performance optimization: using the predictive model as a cost function in optimization algorithms - such as Genetic Algorithms or Bayesian Optimization -to autonomously identify the most suitable parameter combinations. The purpose is to simultaneously satisfy competing engineering criteria, such as maximizing Material Extraction Rate and minimizing Surface Roughness.
Additionally, a third goal of applying advanced training techniques is proposed to explore and evaluate advanced strategies to improve the accuracy and robustness of the model, such as synthetic data generation, sliding-window cropping, regularization techniques, transfer learning and ensembling; with the goal of optimizing the model's capability, even when experimental data are limited or present variability.
During its development, this PFG will allow the acquisition of highly demanded technical skills, such as the use of AI and ML in real problems, multi-objective optimization, the creation of digital twins or the advanced handling of data instructions and Python programming libraries. It will also enhance core topic transversal skills such as critical analysis, complex problem solving and technical communication.
Overall, the work aims to result in an intelligent system that not only predicts, but also provides a decision support tool in industrial automation environments oriented to Industry 4.0.
Academic Supervisor:
Isabel Ayerdi - Aitor Larrañaga Jaio
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT: Materials and Manufacturing Division: Precision Laser Manufacturing group.
subjectarea :
Industrial Automation, Optical Metrology, Profilometry, Materials Characterization, Quality Control, Data Science, Artificial Intelligence.
Description and Objectives:
Optimization and control of laser processes using AI models requires vast data sets linking entrance parameters (power, scan speed, frequency, pitch, etc.) to output quality metrics. The student will collaborate in the creation of a high precision micromachining database from samples etched with various laser conditions.
The main task of the student will be the development and standardization of a methodological automation tool that interacts with the Sensofar S Neox 3D profilometer to massively and repeatably characterize laser micromachining samples. The student will have to configure and implement the routines in the Sensofar software to automate the acquisition of 3D profilometry data and the subsequent processing for the extraction of core topic metrics (depth, roughness, angles, etc.).
This process will eliminate the need for manual measurements, creating a clean, structured and robust data stream that will feed a database for AI creation. If automation is achieved quickly, the project will include a basic AI implementation phase on the data generated in Python.
Objectives:
-
Standardize and document the acquisition protocol using the SensoSCAN MMR (Multiple Measurement Routine) for the automation of the XY stage and measurement sequence.
-
Develop and implement Analysis Recipes in SensoPRO for the automatic calculation and extraction of quality metrics (roughness, depth, wall angles) from the data obtained.
-
Create the data workflow that combines the process parametersentrance) with the quality metrics (output) in a structured dataset ready for Machine Learning.
If time permits, implement a simple Machine Learning algorithm to perform the first quality prediction on the generated dataset.
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcárcel García
department Tecnun CEIT:
ICT Division
subjectarea :
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science
Description and Objectives:
development of a Python application to automate exploratory data analysis (EDA) and predictive regression modeling.
The goal is to build a tool able to read a database (CSV/SQL), automatically classify variables (numerical, categorical), perform univariate and bivariate statistical studies (correlations, graphs) and, finally, automatically apply and compare regression models for a variable of interest. The goal is to offer a robust software for the quick start of Data Science projects.
Proposed Activities:
-
Review of AutoEDA and AutoRegression techniques.
-
Intake module : Data reading and automatic classification of variables.
-
EDA module : Implementation of statistical studies and automatic graphs (univariate and relationship between variables).
-
Regression module : Automatic preprocessing and fitting/comparison of multiple regression algorithms (simplified AutoML).
Username interface: development of an interface (e.g., Shiny) for the visualization of results and insights.
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcárcel García
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT - ICT Division
area subject:
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science
Description and objectives:
The maintenance scheduling problem, known as the Maintenance Scheduling Problem or Maintenance Scheduling Problem, consists of organizing maintenance activities within a schedule in an optimal manner. This problem seeks to minimize interruptions and operating costs by ensuring that both preventive and corrective maintenance are performed at the appropriate times.
The goal of this final Degree project is to develop an optimization tool that addresses the efficient scheduling of maintenance schedules. The tool will be developed preferably in Python, with additional Matlab or R options.
Proposed activities for the student:
Bibliographic review of the most common optimization problems and algorithms applied in maintenance scheduling.
2. Mathematical formulation of the problem, establishing the relevant criteria and restrictions.
3. Implementation of the solution using a heuristic optimization algorithm or open source solvers.
4. Analysis of results and comparison of the effectiveness of the applied approach , with recommendations for its use in different maintenance situations.
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcárcel García
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT - ICT Division
area subject:
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science
Description and objectives:
The application of time-dependent covariates in survival analysis has improved the prediction of time to default in behavioral credit scoring models. However, when these covariates are endogenous, two problems occur: estimation bias and the lack of a framework to predict the future values of the event and the covariates.
Joint models are a statistical approach that simultaneously integrates longitudinal and survival data, allowing to model the joint evolution of an event of interest (such as time to default) and time-dependent endogenous covariates. This project explores for the first time the application of discrete-time joint models to credit scoring, and proposes a novel extension by including autoregressive terms in the endogenous covariates.
The project will apply these methods to U.S. mortgage data, evaluating whether discrete-time joint models improve predictive accuracy compared to traditional survival models and whether performance is optimized by including an autoregressive term.
Proposed activities for the student:
1. Literature review on joint models and their application in credit scoring.
2. Mathematical formulation of the joint model in discrete time.
3. Implementation of the model in R or Python.
4. Analysis of results, comparing predictive performance against other models.
This project will allow the student to explore advanced statistical modeling techniques applied to financial data and improve predictions in the context of credit risk.
Academic Supervisor:
Dr. Carlos Alejandro Peñuelas Angulo
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT - ICT Division
subjectarea :
Information security, data analysis
Description and objectives:
The overall purpose of this project is the design and implementation of an architecture that offers data analysis functions (Machine Learning, data mining, etc.) as a service implementing mechanisms for the preservation of data privacy, also known as Privacy Enhancing Technologies (PETs). This can include from the use of advanced cryptographic mechanisms to federated learning.
The activities expected to be carried out during the execution of this project are:
-
Analyze examples of PETs applied to data analysis.
-
Design an architecture for privacy-preserving data analysis as a service.
-
Implement the architecture using state-of-the-art technologies.
Academic Supervisor:
Saioa Arrizabalaga
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT - ICT Division. data analysis and Information Management Group
subjectarea :
software development , Privacy, Code automation, containers.
Description and objectives:
-
Fides is an open source privacy management platform that enables the enforcement of privacy standards at the code level. Fides tools allow you to tag system privacy features, orchestrate compliance with programmatic rights, and audit staff identifiable information stored in all systems and application infrastructures. Fides in turn supports all major privacy regulations (e.g. GDPR, CCPA and LGPD), and standards such as ISO 19944 by default.
-
This project seeks the automated implementation of the Fides platform in a practical use case, so that a consistent and versioned definition of the privacy features and resources of this system can be created and used as part of a CI/CD pipeline to process privacy requests.
Academic Supervisor:
Saioa Arrizabalaga
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT - ICT Division. data analysis and Information Management Group
area thematic:
development Software, Security.
Description and objectives:
Monitoring and observability tools are widely used nowadays to have a control of the processes running in our Kubernetes cluster. Most of these tools only provide basic monitoring and observability of the Kubernetes cluster, but few of them apply detection and countermeasure. This scenario makes the ability to monitor the protection of a cluster against attacks very difficult leave. On the other hand, we have tools that offer finding of attacks and alerts, but without applying any countermeasure on it. This project has as goal the development of an alert, finding and countermeasure tool for industrial environments, and the integration of this tool with third party tools, capable of solving the above mentioned problems. These functionalities should be integrated into a custom Kubernetes cluster to monitor and protect the cluster from external attacks.
Academic Supervisor:
Saioa Arrizabalaga
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT - ICT Division. data analysis and Information Management Group
area thematic:
Industrial process modeling. Cybersecurity.
Description and objectives:
Hybrid testbeds allow the study of offensive and defensive cybersecurity mechanisms in industrial environments and also their impact on the process under attack or to be defended.
This project would be focused on the generation of digital twins for industrial systems (e.g. wind turbines, water distribution networks...), based on existing Simulink models. The student will have to map sensors/actuators on the models, define operating states (normal, abnormal) to improve testbed monitoring and response capabilities, analyze potential system cybersecurity threats and develop mitigation strategies. Simulink models will be modified so that they can be integrated into the virtualized testbed so that they can be operated in real time.
Academic Supervisor:
Saioa Arrizabalaga
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT - ICT Division. data analysis and Information Management Group
area Thematic:
5G, Kubernetes, Cloud Computing, Virtualization.
Description and Objectives:
The adoption of Cloud Native in 5G telecom systems has been identified as a good candidate to reduce cost, improve system agility and the role of 5G services. Based on the 3GPP standard, the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) has published the reference letter architecture of NFV tailored to Cloud Native environments and to enhance the framework of NFV, including, containers, load balancers and other elements as part of the architecture of reference letter.
This work pursues the validation of container technology on the MANO platform hosted at ETSI, in a CN environment, so that the results obtained in the work can help to encourage users and operators to use KNFs and thus taking advantage of container technologies.
Academic Supervisor:
Saioa Arrizabalaga
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT - ICT Division. data analysis and Information Management Group
subjectarea :
software development , Security.
Description and objectives:
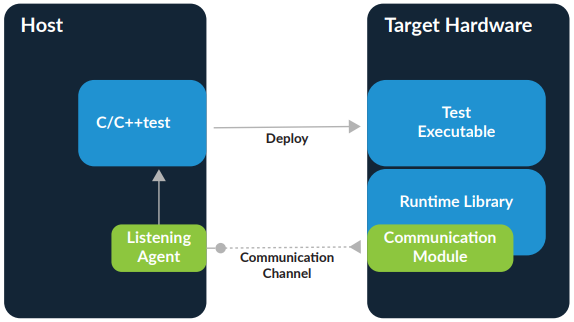
CI/CD is increasingly popular in embedded software development . However, projects are often constrained in a way that they are not in application (e.g., web) development . In addition to the physical and computational limitations of the target hardware platform, there are market limitations. The embedded software market has unique requirements for security, privacy and extremely long life cycles (e.g., products can remain on the market for decades). At the development level, embedded software is not much different than typical application development (e.g., web), requiring IDEs, compilers, static and dynamic analysis and dynamics tools. However, the tools typically address the architectures on which they work (host vs. target environment). Compiler-level automation uses the same techniques, but when code execution is involved, the host/target barrier becomes significant. Code execution automation requires special software development support. Software test automation is more challenging due to the complexity of initiating and testing on embedded targets, not to mention the limited access to the target hardware that software teams have. This project aims to take a first approach to basic CI/CD development on embedded systems. Thus, given a basic development in C/C++, we intend to pass this code through testing, security checks and compilation (CI) stages, and then perform an automated submission on a device (e.g. a microcontroller), not without first performing functional testing (CD).
Academic Supervisor:
Ainhoa Rezola
department CEITTecnun:
Tecnun - department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering
subjectarea :
digital electronicdesign , embedded systems, data processing.
Description and objectives:
The digital core of the RFID label currently under development is composed of multiple functional blocks. To facilitate diagnostics and troubleshooting, it is essential to implement a debugging interface.
The goal of this Final Degree project is to design and develop such an interface with the following functionalities: capture core topic signals from each functional block and serialize them for transmission through a single port (or several, depending on time constraints), ensure that the output is well structured to allow easy identification of each signal, and develop a software tool to extract and interpret these signals.
Knowledge of VHDL and basic programming (Python or MATLAB) is required.
Academic Supervisor:
Ainhoa Rezola
department CEITTecnun:
Tecnun - department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering
SUBJECTarea :
design digital electronics, embedded systems, signal processing.
Description and objectives:
A customized RFID label with sensing capabilities has been designed, and the next step is to integrate a small processor to extend the computational functionalities, especially oriented to the processing of sensor data.
The student will collaborate with the principal researcher in the process of integrating the processor with the labels IP.
Knowledge of VHDL is required.
Academic Supervisor:
Ainhoa Rezola
department CEITTecnun:
Tecnun - department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering
area thematic:
Programación de sistemas embebidos, tratamiento de datos, aplicaciones software
Description and objectives:
A customized RFID label with integrated sensing capabilities is available. The goal of this Final Degree project is to develop a software application that allows to extract and organize the data generated by the label, adapting the data structure depending on the issue and subject of sensors involved.
The student will work with the firmware of both the RFID reader and the label itself, using the API and sample code provided. The main tasks include: development a custom application to interact with the RFID label , extracting the bits related to the sensors, and structuring the data to transform the raw bits into meaningful values.
Knowledge of C/C++ programming is required.
Academic Supervisor:
Diego Borro
department CEITTecnun:
CEIT - Vision and Robotics
Description and objectives:
The goal of the project is to analyze in 3D industrial parts to reconstruct the geometry and make a dimensional control (check if the geometry meets the designed tolerances). Before analyzing the image, it will also be necessary to study the specific application to choose the optimal hardware components (luminaire, optics, laser and camera).
Offer active only when laboratories can be attended in person.
Academic Supervisor:
Diego Borro
department CEITTecnun:
CEIT - Vision and Robotics
Description and objectives:
The goal of the project is to use the Inspect Express tool (from Teledyne Dalsa) to analyze in 2D industrial parts and find defects. This tool allows to program the image analysis algorithms in a visual way through its graphical interface. Before analyzing the image, it will also be necessary to study the specific application in order to choose the optimal hardware components (luminaire, optics and camera).
Offer active only when laboratories can be attended in person.
Academic Supervisor:
Javier Cejudo
department CEITTecnun:
CEIT - ICT Division
subjectarea :
Coding and firmware, IoT, electronic design , embedded systems, wireless communications, industrial automation, security.
Description and objectives:
Remote FPGA programming from a microcontroller, without the need to use a specific programmer. The main goal is to implement the necessary logic in an embedded system subject microcontroller to act as FPGA programmer. The necessary wireless communications (Bluetooth, 4G...) must also be implemented to be able to perform this programming remotely and be accessible from anywhere in the world.
It is a project that proposes to work on physical elements in order to test and promote applied practical skills.
Academic Supervisor:
Iñigo Adin
department CEITTecnun:
CEIT - ICT Division
subjectarea :
Intelligent surfaces, Wireless communications, Electromagnetic simulation, State of the art, Defense, Security, Selective concealment, Electronic design .
Description and objectives:
Embark on a pioneering Final Project exploring the future of communications and defense through programmable wireless environments. This project dives into the technologies that are redefining the interaction with electromagnetic waves, such as Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS), metamaterials and the emerging Multifunctional RIS (MF-RIS) that integrates sensing capabilities for autonomous operation. Your mission statement will be to perform a comprehensive state-of-the-art review, analyzing the fundamental techniques and trends presented in the sources, from passive beamforming and channel optimization to challenges in wideband channels and near-field phenomena. From this research, you will be expected to propose innovative applications that leverage these capabilities not only to revolutionize 6G communications, improving coverage, security and efficiency, but also to develop cutting-edge defense systems, including secure tactical communications, stealth technologies to reduce radar and acoustic detectability, and new forms of electronic warfare and environmental surveillance.
Academic Supervisor:
Dr. Emilio Sánchez Tapia
department CEITTecnun:
CEIT - Vision and Robotics
subjectarea :
Industrial automation/robotics
Description and objectives:
This Degree final project is born as a direct continuation of a previous work in which the same unscrewing operation was successfully automated. In that first phase, the control architecture was based on a traditional industrial system, using a PLC to govern the KUKA robot. Having validated the mechanical and vision feasibility of the system, this new project focuses on exploring an alternative and more flexible control architecture.
The new goal is therefore to approach the control from two different perspectives in order to compare its performance. Instead of using the PLC, a specialized controller, extremely reliable and designed to operate in real time, the same process will be implemented using ROS (Robot Operating System) on a conventional computer. ROS is not an operating system like Windows, but a set of open source software tools that greatly facilitates the programming of robots and the integration of components such as cameras or artificial intelligence algorithms. The final scope is to evaluate and quantify the advantages and disadvantages of each approach: the robustness and determinism of the industrial PLC versus the flexibility, speed of development and processing power offered by a system based on ROS and a PC.
Tasks to be performed by the student:
-
Familiarization with previous work
-
Learning the programming technique of the Kuka Issy robot.
-
Learning to use the ROS operating system
-
Programming from ROS of the execution of a sequence of paths for screwing/unscrewing (language to be defined, it can be in Python or C++).
-
Testing and evaluation of the performance achieved
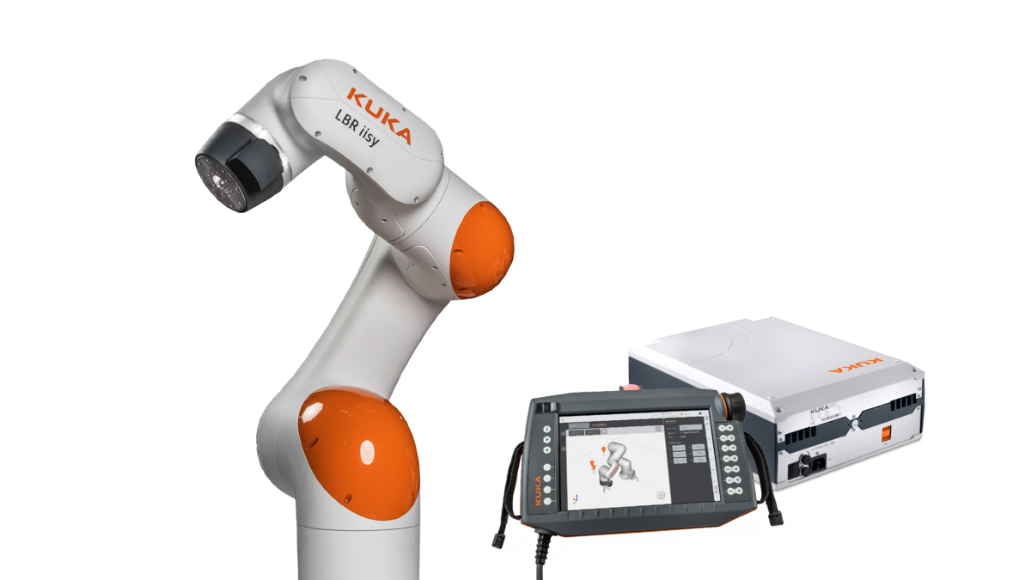

Photo of the KUKA collaborative robot to be used in the PFG.
Academic Supervisor:
Adam Podhorski
subjectarea :
Communication systems
Description and objectives:
The proposed PFG combines drones, signal processing and machine vision. It is part of a project to measure external noise from one or more drones, creating an acoustic camera. An acoustic camera is a device that measures the noise level coming from different directions and visualizes it in the form of a heat map together with the actual image. An example can be seen here: GFaI acoustic camera.
What does the project consist of?
- Design and build a microphone array with an integrated camera.
- Capture signals with PDM microphones (microphones with digital output).
- Integrate the system in a drone and perform test flights in the sports center with real noise sources.
- Process the acquired signals in Matlab to obtain the acoustic image.
Academic Supervisor:
Santiago M Olaizola
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
Materials and Manufacturing Division: Precision Laser Manufacturing group.
area subject:
Industrial manufacturing processes
Description and objectives:
Our research activity is focused on laser processing of materials. For this purpose, we use ultra-short laser pulses (femtosecond lasers), capable of producing very precise Structures on material surfaces with a very high definition of the order of micrometer. This is made possible by the "cold ablation" processing regime. High definition surface textures can be used for a variety of applications, such as friction management, plastic injection molds, implants, metrology of self-cleaning objects, antennas, etc.
The research project offered in this group covers the fabrication, measurement and modeling of the Structures for a selected application. The specific nature of the project depends on the duration of the placement and the student's background. For example:
Industrial technologies engineering: laser modification of stainless steel to control surface hydrophobicity, design and laser process programming.
Telecommunication engineering: analysis of the predictability of periodic corrugations on surfaces produced by femtosecond lasers, analysis of results, laser beam control.
Field: laser applications
requirementsPhysics: solid knowledge of physics. Python programming skills are recommended.
Academic Supervisor:
Saioa Arrizabalaga
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
ICT Division. Group of data analysis and Information Management
area Thematic:
5G, Kubernetes, Cloud Computing, Virtualization.
Description and Objectives:
The adoption of Cloud Native in 5G telecom systems has been identified as a good candidate to reduce cost, improve system agility and the role of 5G services. Based on the 3GPP standard, the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) has published the reference letter architecture of NFV adapted to Cloud Native environments and to enhance the framework of NFV, including, containers, load balancers and other elements as part of the architecture of reference letter.
This work pursues the validation of container technology on the MANO platform hosted at ETSI, in a CN environment, so that the results obtained in the work can help to encourage users and operators to use KNFs and thus taking advantage of container technologies.
Academic Supervisor:
Saioa Arrizabalaga
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
ICT Division. Group of data analysis and Information Management
area thematic:
development Software, Security.
Description and Objectives:
CI/CD is increasingly popular in embedded software development . However, projects are often constrained in a way that they are not in the development of applications (e.g., web). In addition to the physical and computational limitations of the target hardware platform, there are market limitations. The embedded software market has unique requirements security, privacy, and extremely long life cycles (e.g., products can remain on the market for decades). At the level of development, embedded software is not much different than development from typical applications (e.g., web), requiring IDEs, compilers, static and dynamic analysis and dynamics tools. However, the tools typically address architectures on which they work (host vs. target environment). Compiler-level automation uses the same techniques, but when code execution is involved, the host/target barrier becomes significant. Code execution automation requires special support development of software. Software test automation is more challenging due to the complexity of initiating and testing on embedded targets, not to mention the limited limited access to the target hardware that software teams have. This project, aims to carry out a first approach to the basic development CI/CD on embedded systems. Thus, given a basic development in C/C++, it is intended to pass this code through stages of testing, security checks and compilation (CI), to then perform an automated submission on a device (e.g. a microcontroller), but not before also performing functional testing (CD).
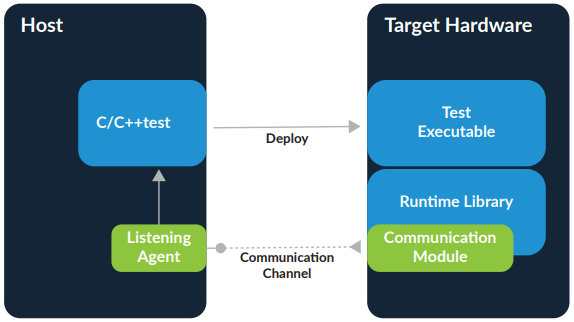
Academic Supervisor:
Saioa Arrizabalaga
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
ICT Division. Group of data analysis and Information Management
area thematic:
Industrial process modeling. Cybersecurity.
Description and objectives:
Hybrid testbeds allow the study of offensive and defensive cybersecurity mechanisms in industrial environments and also their impact on the process being attacked or defended.
This project would be focused on the generation of digital twins for industrial systems (such as wind turbines, water distribution networks...), using existing Simulink models. The student will have to map sensors/actuators on the models, define operating states (normal, abnormal) to improve testbed monitoring and response capabilities, analyze potential system cybersecurity threats and develop mitigation strategies. Simulink models will be modified so that they can be integrated into the virtualized testbed so that they can be operated in real time.
Academic Supervisor:
Saioa Arrizabalaga
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
ICT Division. Group of data analysis and Information Management
area thematic:
development Software, Privacy, Code Automation, Containers.
Description and objectives:
Fides is an open source privacy management platform for enforcing privacy standards at the code level. Fides tools allows to tag system privacy features, orchestrate programmatic rights enforcement and audit staff identifiable information stored in all systems and application infrastructures. Fides in turn supports all major privacy regulations (e.g. GDPR, CCPA and LGPD), and standards such as ISO 19944 by default.
This project seeks the automated implementation of the Fides platform in a practical use case, so that a consistent and versioned definition of the privacy features and resources of this system can be created, being used as part of a CI/CD pipeline to process privacy requests.
Academic Supervisor:
Saioa Arrizabalaga
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
ICT Division. Group of data analysis and Information Management
area thematic:
development Software, Security.
Description and objectives:
Monitoring and observability tools are widely used nowadays to have a control of the processes running in our Kubernetes cluster. Most of these tools only provide basic monitoring and observability of the Kubernetes cluster, but few of them apply detection and countermeasure. This scenario makes the ability to monitor the protection of a cluster against attacks very difficult leave. On the other hand, we have tools that offer finding of attacks and alerts, but without applying any countermeasure on it. This project has as goal the development of an alert, finding and countermeasure tool for industrial environments, and the integration of this tool with third party tools, capable of solving the above mentioned problems. These functionalities should be integrated into a custom Kubernetes cluster to monitor and protect the cluster from external attacks.
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcárcel García
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
ICT Division. Group of data analysis and Information Management
area subject:
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science
Description and objectives:
The application of time-dependent covariates in survival analysis has improved the prediction of time to default in behavioral credit scoring models. However, when these covariates are endogenous, two problems occur: estimation bias and the lack of a framework to predict the future values of the event and the covariates.
Joint models are a statistical approach that simultaneously integrates longitudinal and survival data, allowing to model the joint evolution of an event of interest (such as time to default) and endogenous time-dependent covariates. This project explores for the first time the application of discrete-time joint models to credit scoring, and proposes a novel extension by including autoregressive terms in the endogenous covariates.
The project will apply these methods to U.S. mortgage data, evaluating whether discrete-time joint models improve predictive accuracy compared to traditional survival models and whether performance is optimized by including an autoregressive term.
Proposed student activities:
-
Literature review on conjoint models and their application in credit scoring.
-
Mathematical formulation of the model set in discrete time.
-
Implementation of model in R or Python.
-
Analysis of results, comparing predictive performance against other models.
This project will allow the student to explore advanced statistical modeling techniques applied to financial data and improve predictions in the context of credit risk.
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcárcel García
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
ICT Division. Group of data analysis and Information Management
area subject:
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science
Description and objectives:
The maintenance scheduling problem, known as the Maintenance Scheduling Problem, consists of optimally organizing maintenance activities within a schedule. This problem seeks to minimize interruptions and operating costs, ensuring that both preventive and corrective maintenance are performed at the right times.
The goal of this end of Degree project is to develop an optimization tool that addresses efficient scheduling of maintenance schedules. The tool will be developed preferably in Python, with additional Matlab or R options.
Proposed student activities:
-
Bibliographic review of the most common optimization problems and algorithms applied in maintenance scheduling.
-
Mathematical formulation of the problem, establishing the relevant criteria and restrictions.
-
Implementation of the solution using a heuristic optimization algorithm or open source solvers.
-
Analysis of results and comparison of the effectiveness of the applied approach , with recommendations for its use in different maintenance situations.
Academic Supervisor:
Markos Losada
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
Transport and Energy Division: Transport and Sustainable Mobility Group.
area subject:
design electronic, coding, data processing
Description and objectives:
The approach of this final work of Degree focuses on the analysis of advanced distance estimation technologies that could be integrated into a system for a wristband to analyze the game of Padel. The project is divided into several phases, starting with a comprehensive analysis of existing commercial systems, evaluating their advantages and proposing improvements. The review of current technologies such as time-of-flight (ToF), Lidar and ultrasound sensors is fundamental to select the most appropriate technology for this purpose. The proposal for improvement will include technology selection, the development of a specific algorithm and system integration, considering factors such as size, cost and power consumption. The goal is for the student to not only gain knowledge about these technologies, but also to propose a concrete solution that can be implemented.
In the implementation phase, the student will be responsible for integrating the selected sensors and developing a system capable of detecting a matrix of points to accurately estimate distances. The results obtained will be analyzed to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm and determine the feasibility of its implementation in a commercial product. This project not only seeks to improve the paddle tennis playing experience, but also to explore potential applications of these technologies in other fields, such as weighing or wagon monitoring.
Academic Supervisor:
Iñigo Adín
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
Transport and Energy Division: Transport and Sustainable Mobility Group.
area subject:
Artificial intelligence learning, coding, data processing.
Description and objectives:
This final work of Degree has as main goal the development and the implementation of machine learning models in low power microcontrollers, specifically of the STM32 family, using TensorFlow Lite. The project focuses on the application of these models in the transportation sector, with a particular approach on the analysis and improvement of automatic braking systems.
To achieve this goal, the student should:
Training in Tools and Technologies:
Acquire knowledge of TensorFlow Lite for microcontrollers, through Machine Learning resources such as Andrew Ng's documentation, and "Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras and TensorFlow", as a foundation and using Wes McKinney's "Python for the data analysis" as reference letter for management and data analysis.
development of Machine Learning Models:
Design and train machine learning models that can be optimized for execution on low-power microcontrollers.
Evaluate the performance of these models in terms of accuracy, efficiency and energy consumption. For this purpose, data will be collected with a sensorized brake bench and the models will be trained with them.
Integration in Microcontrollers:
Implement the developed models on STM32 microcontrollers using TensorFlow Lite. Ensure that the integration is efficient in terms of resources and reliability of the results.
Application in the Transportation Sector:
Apply integrated models to improve the automatic braking function in vehicles, analyzing real-time data to optimize system safety and efficiency.
Evaluate the impact of the implementation in test scenarios, adjusting the models as needed to improve performance.
The documentation and results will be organized documenting the references and the process of development. The results obtained will be presented, highlighting the improvements achieved in the automatic braking function and possible future applications of the developed technology.
Academic Supervisor:
Emilio Sanchez Tapia
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
Materials and Manufacturing Division: Robotics and Industrial Control Group.
area thematic:
Robotic Engineering
Description and objectives:
In the context of robotics in the 21st century, the concept of the connected factory arises where machines, mobile robots and humans coexist. Mobile robots may or may not include a robotic manipulator arm or MoMa (MObile MAnipulator). If there is only the mobile robot, it is usually referred to as AMR (Autonomous Mobile Robot) or AGV (Autonomous Guide Vehicle) according to its Degree of freedom in navigation (see figure below).
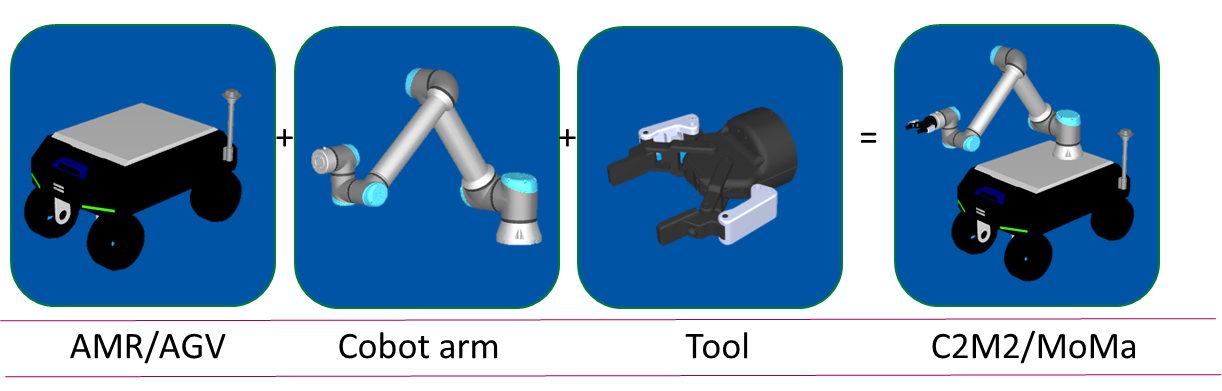
Figure 1: Constituent elements of a platform-mounted collaborative robot (or MoMa).
The main application of this device subject is to increase the level of factory automation in sectors where today automation has leave penetration, such as intralogistics and machine tending. In these scenarios, the robot can move raw materials, products in the manufacturing process or even search for machine replacement parts (such as a cutting head for a CNC). In any case, the MoMa will be able to perform the task either autonomously or as an assistant to a human operator (see figure below).

Figure 2: Factory scenario where a MoMa becomes one more resource of the factory where it can work alone or in collaboration with other human operators.
A likely scenario is that in the factory we will find more than one mobile robot, each of them with different capabilities and probably from different manufacturers. In this case it is important to have software that coordinates the tasks and distributes them appropriately according to the availability and/or capacity of each robot. Such software is known as a robot fleet manager.

Figure 3: A fleet manager coordinates the work of a set of robots.
There are many fleet management solutions on the market, but they are usually proprietary and compatible with only one brand of robot.
The goal of the final project of Degree is to deploy and test an open-source robotic fleet manager. The tests will be done both in simulation and with real robots.
As of essay of this document, it is planned to use open-rmf (Open-RMF: https://www.open-rmf.org/ ) or equivalent, see the following figure.
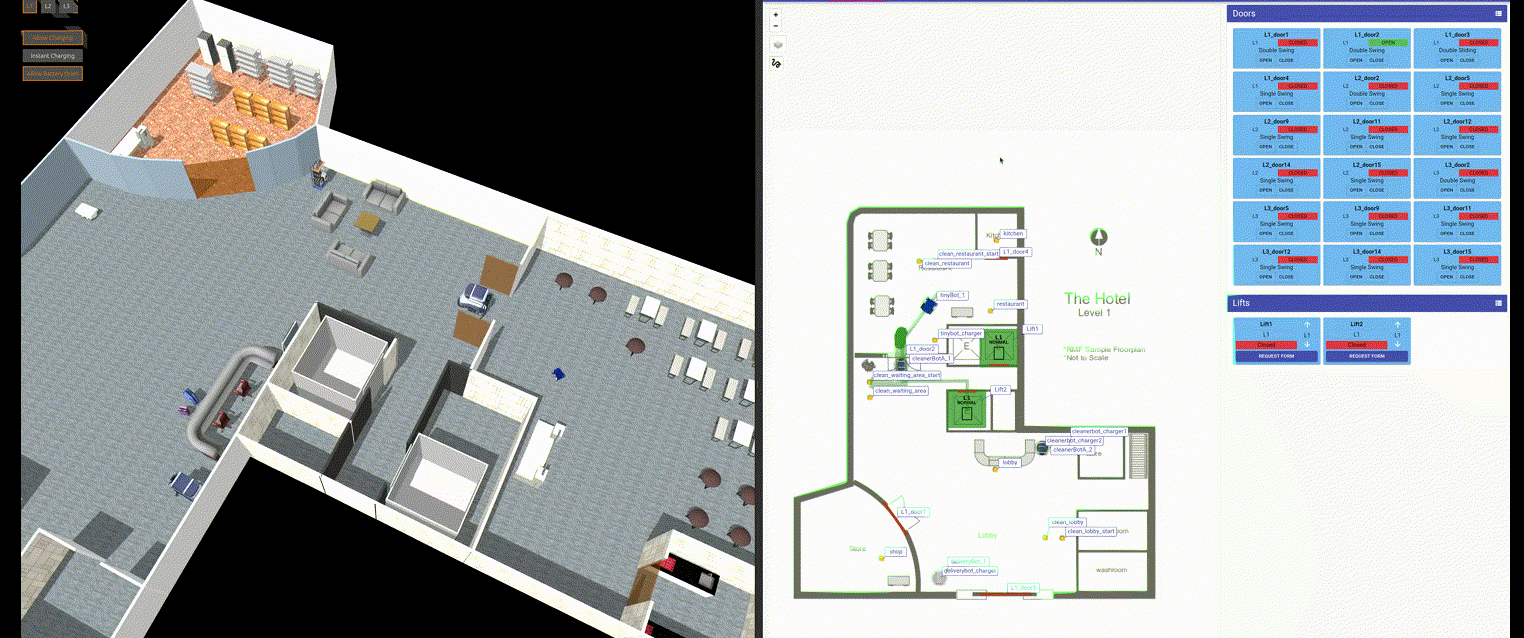
Figure 4: Screenshot of a simulation of coordinated fleets from open-rmf.
It is offered, during the execution of project:
-
Incorporation to the robotics group of researchers from the CEIT
-
Training in the software/hardware tools employed
-
Possibility of a job offer in a company in the sector.
Testbeds are fundamental elements for safety testing. However, a first approach is to verify the feasibility of the Testbed based on the development performance test.
The following work aims to create a Testbed for performance testing based on the integration of the digital twin of a Wind Turbine as Hardware In The Loop (HIL), a virtual PLC as OpenPLC and a set of Modbus clients, which will allow scalability testing. The following figure sample shows an architecture of reference letter with the components involved in the Testbed.
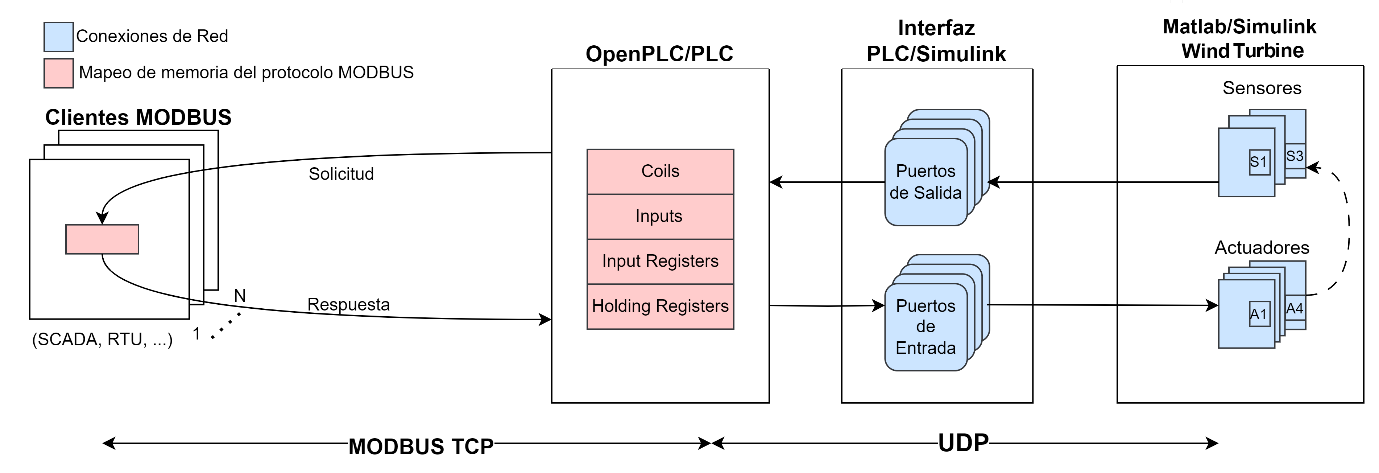
Figure 1: Communication flow.
Specifically, the digital wind turbine twin to be integrated is as follows:
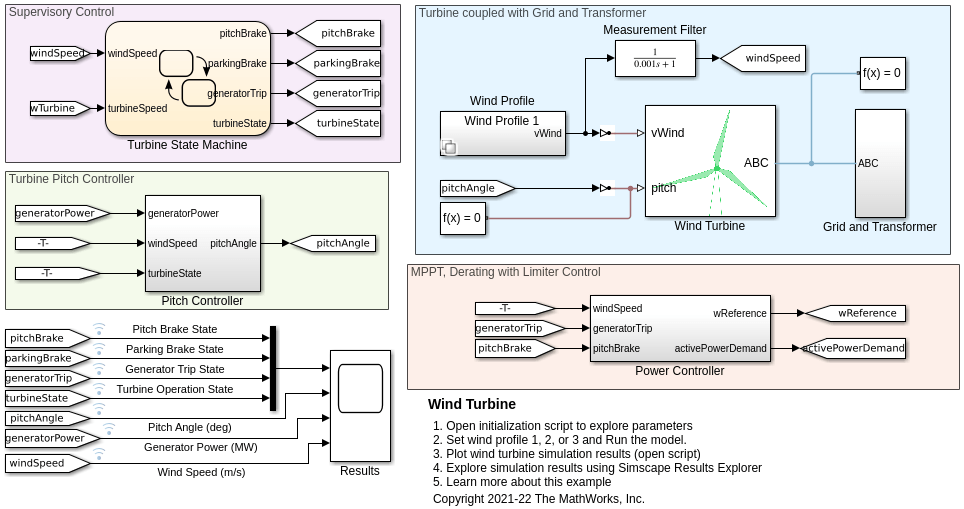
Figure 2: Wind generator created on Matlab Simulink.
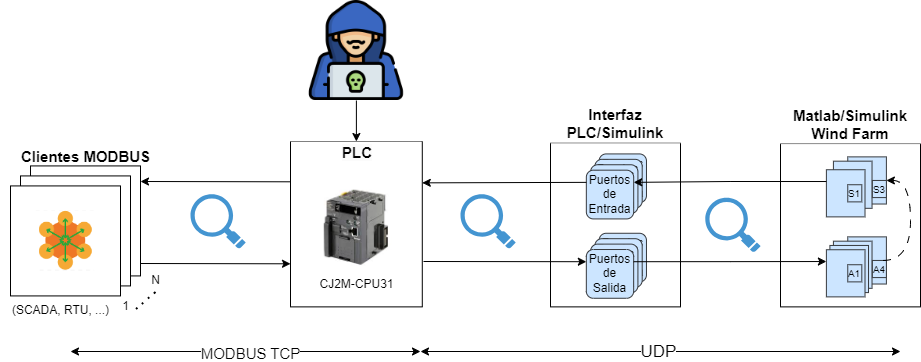
Figure 3: Attacks on virtual/real PLC.
The project would involve a second approach using a real PLC, i.e., swapping the virtual PLC (OpenPLC) for a real Omron PLC. The rest of the experimentation procedures would be identical. In this way one of the environments could be used as a benchmark to establish a comparison with respect to the other. The tasks to be performed are listed below:
- Analyze the archive base, understanding how to generate information flows.
- Package in a container a wind generator developed in Matlab Simulink (see Figure 2).
- Add the necessary components to establish UDP communication between the simulink model (packaged) and the interfaces (see Figure 1).
- Develop the necessary control code in the virtual PLC to enable communication with the wind turbine.
- Connect the virtual PLC to Modbus clients, created using the bookshop pymodbus, to enable performance testing.
- Collection of performance test metrics for analysis.
- Transform the control code created for the virtual PLC into the code needed for the real PLC to enable communication with the wind turbine.
- Connect the actual PLC to Modbus clients, created using the bookshop pymodbus, to enable performance testing.
- Collection of performance test metrics for analysis.
- Collect tools to exploit existing vulnerabilities on the virtual/real PLC (see Figure 3).
- Performing security tests by classifying them according to the pillar of cybersecurity they compromise, e.g., availability, integrity, etc (see Figure 3).
Testbeds are fundamental elements for security testing. In particular, the field of collaborative robotics constitutes a Safety environment of great interest for cybersecurity research. Progress is currently being made in this direction, working on a flow like the one shown in Figure 1 at sample .
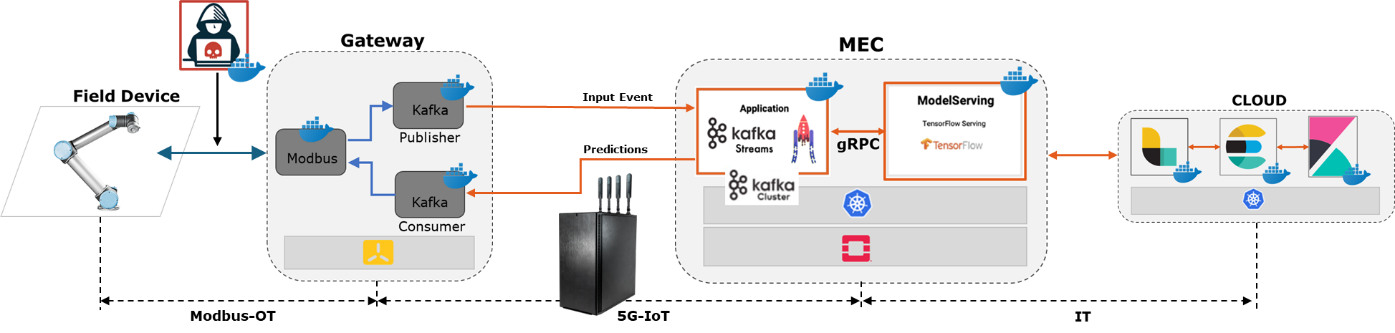
Figure 1: Testbed for cybersecurity testing on collaborative robotics environments.
However, there is still a long way to go in several of these stages. In this paper we intend to study one of them in depth. Specifically, the field device (robot) communication with the IoT Gateway, i.e., the flow shown in Figure 2:
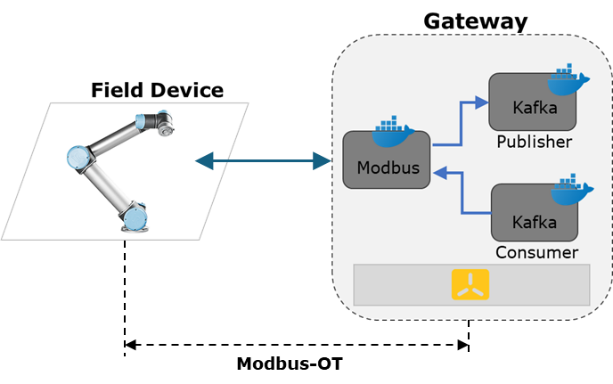
Figure 2: area of Testbed improvement.
1- Since Universal Robots has released a series of simulators, we would be interested to know, which of all is the series or ROBOT_MODEL that would allow us to have greater control over the field device, which translates into greater read/write capability over the device variables.
2- Obtaining and storing records (logs) of the robot as an element core topic for analysis during safety tests. These logs should allow active monitoring of the device.
3- Considering a Raspberry Pi as IoT Gateway, an infrastructure based on K3s will be installed on it. On this K3s infrastructure a microservices based architecture will be deployed which will contain 4 microservices: Modbus client, Kafka Publisher, Kafka consumer, Engine. grade This task will be developed in collaboration with other researchers of the group to carry out an implementation that integrates the CI/CD methodology to enable automatic updates on the Raspberry.
4- A 5G module will be installed on the Raspberry to enable communication with the Amarisoft central. grade This task depends on the purchase process of module.
5- Considering Modbus as the transport protocol between the field device and the IoT Gateway, the following task seeks to improve the code currently generated (packaged in a container) to monitor with certain periodicity the set of variables enabled by the robot.
6- These variables will be collected and sent to a second microservice which uses the protocol Kafka, which should be programmatically optimized to reduce latency and increase throughput. To test this microservice, the test broker exemplified in Figure 3 should be used.
7- A third microservice will be integrated to act as Kafka's publisher, which will also have to be optimized. To test this microservice, the test broker exemplified in Figure 3 should be used.
8- A fourth microservice should be developed to act as a response engine that will depend on the prediction received from the Kafka consumer, based on which it should make decisions that will be transmitted to the Modbus client and transferred to the field device as sample Figure 3.
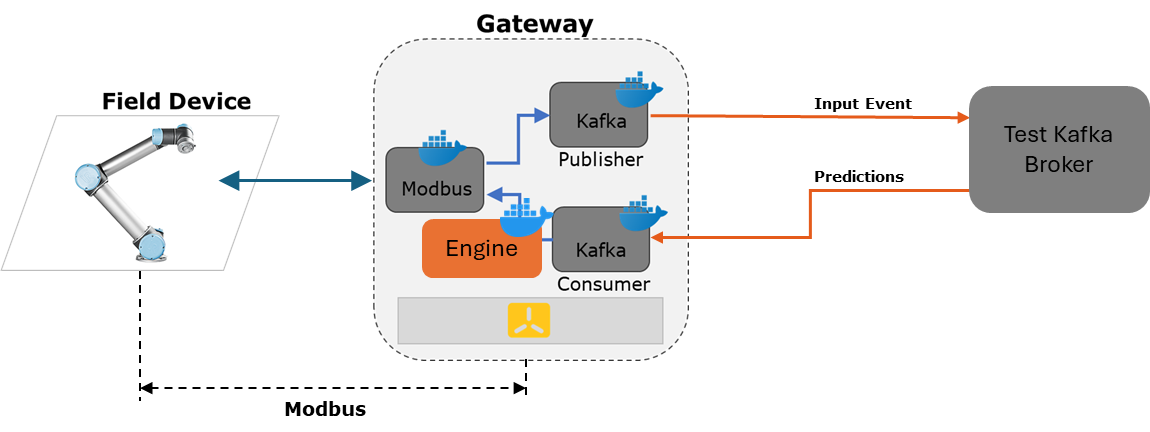
Figure 3: Integration of Engine on Testbed.
9- Integration of the IoT Gateway on the communication flow of the use case as sample Figure 4. grade This task depends on the progress of other researchers in the group.

Figure 4: Testbed with complete communication flow.
Academic Supervisor:
Enrique Castaño Carmona
Division CEIT:
Advance Powder Metallurgy and Laser Manufacturing Group
area thematic:
Computing, modeling and simulation
Description and objectives:
The machining of materials using ultra-short pulse lasers is a very recent technology development and opens multiple possibilities in the field of functional surfaces, such as low friction coefficient surfaces in wind turbines or anti-icing surfaces in aeronautics.
Currently, Ceit is leading a European project in which one of its objectives is to develop a simulation software for the machining process with this subject of lasers. The mathematical modeling of the process is already well advanced, as well as its numerical implementation.
The task of this PFG will be to design and develop the graphical interface with the Username of the simulation program so that its use is easy and intuitive. The student will apply and extend his knowledge of Python programming, GUI (Graphic User Interface) and design UX/UI (User Experience/User Interface) to achieve an interface that allows Username an attractive experience of the simulation program.
Academic Supervisor:
Santiago Figueroa Lorenzo
Division CEIT:
ICT Division. Group of data analysis and Information Management
area thematic:
development Software, Security.
Description and Objectives:
CI/CD is increasingly popular in embedded software development . However, projects are often constrained in a way that they are not in the development of applications (e.g., web). In addition to the physical and computational limitations of the target hardware platform, there are market limitations. The embedded software market has unique requirements security, privacy, and extremely long life cycles (e.g., products can remain on the market for decades). At the level of development, embedded software is not much different than development from typical applications (e.g., web), requiring IDEs, compilers, static and dynamic analysis and dynamics tools. However, the tools typically address architectures on which they work (host vs. target environment). Compiler-level automation uses the same techniques, but when code execution is involved, the host/target barrier becomes significant. Code execution automation requires special support development of software. Software test automation is more challenging due to the complexity of initiating and testing on embedded targets, not to mention the limited limited access to the target hardware that software teams have. This project, aims to carry out a first approach to the basic development CI/CD on embedded systems. Thus, given a basic development in C/C++, it is intended to pass this code through stages of testing, security checks and compilation (CI), to then perform an automated submission on a device (e.g. a microcontroller), but not before also performing functional testing (CD).
Academic Supervisor:
Santiago Figueroa Lorenzo
Division CEIT:
ICT Division. Group of data analysis and Information Management
area thematic:
development Software, Privacy, Code Automation, Containers.
Description and objectives:
Fides is an open source privacy management platform for enforcing privacy standards at the code level. Fides tools allows to tag system privacy features, orchestrate programmatic rights enforcement and audit staff identifiable information stored in all systems and application infrastructures. Fides in turn supports all major privacy regulations (e.g. GDPR, CCPA and LGPD), and standards such as ISO 19944 by default.
This project seeks the automated implementation of the Fides platform in a practical use case, so that a consistent and versioned definition of the privacy features and resources of this system can be created and used as part of a CI/CD pipeline to process privacy requests.
Academic Supervisor:
Santiago Figueroa Lorenzo
Division CEIT:
ICT Division. Group of data analysis and Information Management
area thematic:
development Software, Security.
Description and objectives:
Monitoring and observability tools are widely used nowadays to have a control of the processes running in our Kubernetes cluster. Most of these tools only provide basic monitoring and observability of the Kubernetes cluster, but few of them apply detection and countermeasure. This scenario makes the ability to monitor the protection of a cluster against attacks very difficult leave. On the other hand, we have tools that offer finding of attacks and alerts, but without applying any countermeasure on it. This project has as goal the development of an alert, finding and countermeasure tool for industrial environments, and the integration of this tool with third party tools, capable of solving the above mentioned problems. These functionalities should be integrated into a custom Kubernetes cluster to monitor and protect the cluster from external attacks.
Academic Supervisor:
Santiago Figueroa Lorenzo
Division CEIT:
ICT Division. Group of data analysis and Information Management
area Thematic:
5G, Kubernetes, Cloud Computing, Virtualization.
Description and Objectives:
The adoption of Cloud Native in 5G telecom systems has been identified as a good candidate to reduce cost, improve system agility and the role of 5G services. Based on the 3GPP standard, the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) has published the reference letter architecture of NFV tailored to Cloud Native environments and to enhance the framework of NFV, including, containers, load balancers and other elements as part of the architecture of reference letter.
This work pursues the validation of container technology on the MANO platform hosted at ETSI, in a CN environment, so that the results obtained in the work can help to encourage users and operators to use KNFs and thus taking advantage of container technologies.
Academic Supervisor:
Gorka de Miguel
Division CEIT:
Transportation and sustainable mobility
area subject:
Telecommunication engineering
Description and objectives:
The use of positioning systems is becoming more and more common in the daily life of both people and companies, which integrate them in their systems as core topic pieces when it comes to want a safety and efficiency Degree that meets market expectations. In this sense, the major players in the railway sector (CAF, Thales, SNCF, Siemens, etc.) are devoting great efforts to the precise and continuous positioning of their trains.
As its positioning systems are mainly based on GPS/GNSS technologies, the main challenge for challenge is to locate the receivers in indoor environments, where the satellite signal is degraded. Currently, Ceit is involved in a major European initiative that seeks to develop total positioning systems that work both indoors and outdoors, and that do so accurately and continuously, in order to reach the highest level of maturity on the road to the autonomous train Degree .
The task of this PFG would be to design and implement a WiFi-based positioning system that operates indoors and can be further merged with GPS/GNSS technologies.
Academic Supervisor:
Gorka de Miguel
Division CEIT:
Transportation and sustainable mobility
area subject:
Telecommunication engineering
Description and objectives:
The use of positioning systems is becoming more and more common in the daily life of both people and companies, which integrate them in their systems as core topic pieces when it comes to want a safety and efficiency Degree that meets market expectations. In this sense, the major players in the railway sector (CAF, Thales, SNCF, Siemens, etc.) are devoting great efforts to the precise and continuous positioning of their trains.
As its positioning systems are mainly based on GPS/GNSS technologies, the main challenge for challenge is to locate the receivers in indoor environments, where the satellite signal is degraded. Currently, Ceit is involved in a major European initiative that seeks to develop total positioning systems that work both indoors and outdoors, and that do so accurately and continuously, in order to reach the highest level of maturity on the road to the autonomous train Degree .
The task of this PFG would be to conduct a study of the use of 5G technology for indoor positioning and to implement a 5G-based positioning algorithm that makes use of synthetic signals simulated using Matlab.
Academic Supervisor:
Gorka de Miguel
Division CEIT:
Transportation and sustainable mobility
area subject:
Telecommunication engineering
Description and objectives:
The use of positioning systems is becoming more and more common in the daily life of both people and companies, which integrate them in their systems as core topic pieces when it comes to want a safety and efficiency Degree that meets market expectations. In this sense, the major players in the railway sector (CAF, Thales, SNCF, Siemens, etc.) are devoting great efforts to the precise and continuous positioning of their trains.
As its positioning systems are mainly based on GPS/GNSS technologies, a major challenge for challenge is to obtain continuous centimeter accuracies on a global basis. Currently, Ceit is involved in a major European initiative to develop total positioning systems that are capable of locating trains ultra-precisely on their mission statement along the tracks, in order to reach the highest Degree of maturity on the road to the autonomous train.
The task of this GFP would be to implement an algorithm for decoding HAS augmentation signals from Galileo satellites for ultra-precise positioning, and its application to an already functional Matlab positioning algorithm based on GPS/GNSS signals.
Academic Supervisor:
Yuemin Ding
department Tecnun:
Electrical and Electronic Engineering
area thematic:
Telecommunication
Description and objectives:
Online monitoring and data collection in ultra-remote areas is specifically meaningful to investigate the local characteristics of climate change, biodiversity evolution, etc. It is also very important to prevent huge disasters, such as wildfires. However, online monitoring and data collection in ultra-remote areas have been challenging during the past decades. A major challenge is the lack of digital infrastructure for communication and data collection. However, the emerging satellite networking (such as Starlink) and low-power and long-distance IoT (such as MIoTy) technologies enable an alternate solution for online monitoring and data collection. The aim of this project is to develop a system based on satellite networks and low-power and long-distance IoT to enable online monitoring and data collection in ultra-remote areas.
Academic supervisor:
Leticia Zamora Cadenas - Iker Aguinaga Hoyos.
Division CEIT:
Information and Communication Technologies. Intelligent Systems for Industry 4.0 Group.
area thematic:
Telecommunication/Industrial Engineering
Description and objectives:
Indoor location systems are a booming element in recent years. Whether using radiofrequency technologies, inertial sensors or artificial vision systems, the location of objects or people in interior spaces is an element core topic in many applications (tracking of parts, access to security areas, tracking of people, augmented reality, etc.).
To determine and evaluate the accuracy of a location system, the most common method is to measure guide a number of control points or tests in a controlled environment to determine the accuracy of the system. However, this subject measurement is always subject to measurement errors, human error, and the impossibility of tracking a moving element in real time. Another widespread option, especially when the accuracy is to be evaluated dynamically, is to resort to cost-effective systems that allow the creation of the real path or "ground truth", such as, for example, vision tracking systems. However, it is not always possible to deploy this type of system subject , or the economic means to do so are not always available. Therefore, being able to evaluate the accuracy of indoor positioning systems at a low cost is still a problem that researchers and companies are trying to solve.
Currently Ceit has a line of research associated with positioning systems for indoor spaces, in which it works with various companies to provide solutions to their needs. This is why the need for a ground truth system that is easy to install and not too expensive was born.
The task of this GFP would be to develop a ground truth system, using virtual/augmented reality systems, for subsequent use in evaluating the accuracy of the proprietary indoor location system Ceit. HTC Vice, Oculus Quest and Hololens 2 hardware are available for the development of this system using the Unity3D programming platform. The candidate must have programming skills in C# or similar languages such as C++ or Java.
Academic supervisor:
Emilio Sánchez Tapia
Division CEIT:
Information and communications technologies. Intelligent Systems for Industry 4.0 Group. Vision and Robotics Subgroup
area thematic:
Robotics Engineering
Description and objectives:
Industry 4.0 has paved the way for multiple forms of automation that have as goal improve productivity and optimize work processes. In this context, the aim is to develop an intelligent mobile manipulator: a new robot subject that integrates the technology of an autonomous mobile robot and a highly efficient collaborative robotic arm capable of performing various operations.
The idea of project is to develop a robot that can move, detect and avoid obstacles, explore its environment to recognize objects through artificial vision and perform part handling tasks, being able to interact with operators. With the idea of implementing a digital transformation model , required today in real factory environments, robots, control elements, sensors and other onboard elements will be connected to each other through a digital platform to control the process in real time and from anywhere.
Currently CEIT has already developed a first working prototype (see figure below).
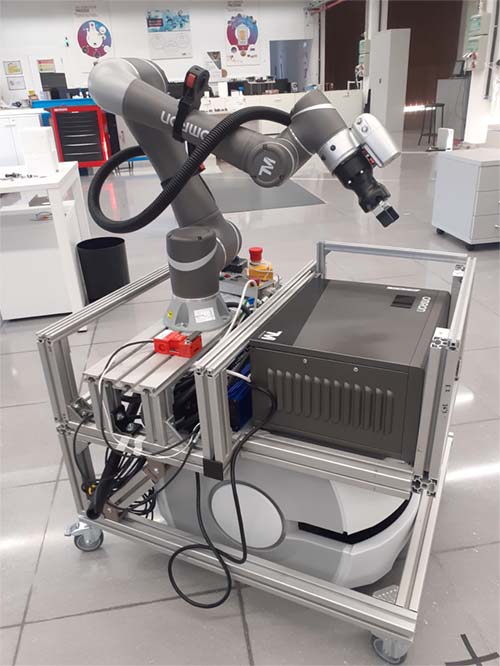

The task of this GFP would be the programming under ROS-2 of a sequence of tasks for the robot to interact with a classic robotic cell. The specific case to be developed will be for the robot to go to a archive of parts to be processed, bring them to the cell, wait for their processing and take them to another storeroom of already sorted parts.
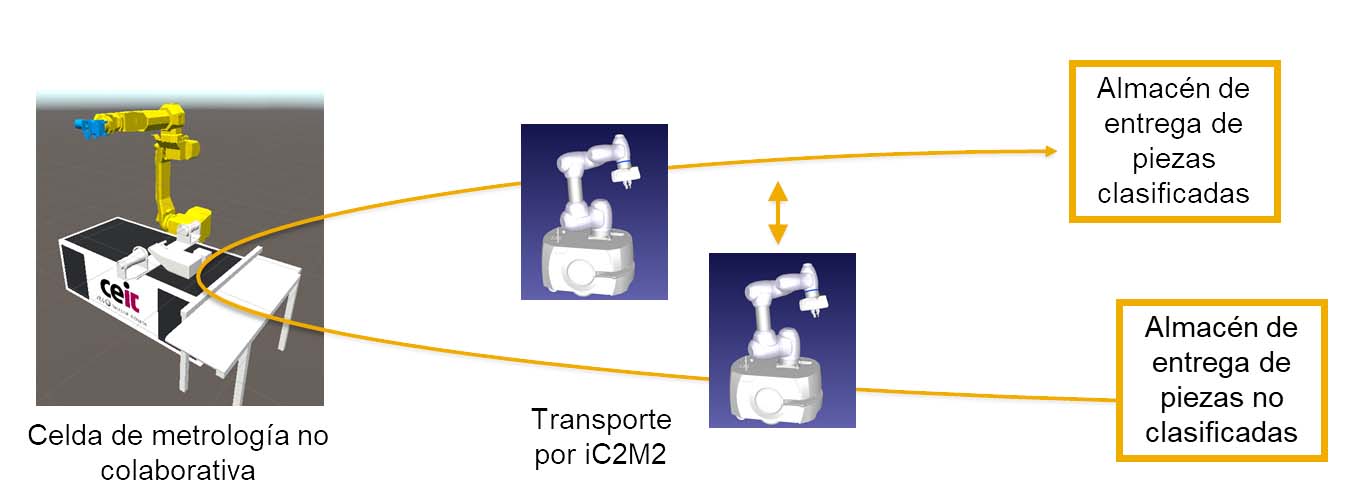
Under this simple task, the concepts of:
- Collaborative mobile robotics
- Machine tending
- Control in force
- Problem of synchronisation of two automatic devices
Programming skills in C/C++, Python or java-script are required.
Academic supervisor:
Diego Borro
Division CEIT:
Intelligent Systems for Industry 4.0
area thematic:
Telecommunication Systems Engineering
Description and objectives:
Copernicus is the world's largest Earth observation programme to date. The programme is a joint initiative of the European Commission and the European Space Agency (ESA) to build an autonomous Earth observation system. The Copernicus programme relies on a family of satellites called Sentinel, owned by the European Union and developed to meet the needs of the Copernicus services and their users.
Every object on the Earth's surface reflects and absorbs energy in a variety of ways. The spectral signature represents the unique way in which a surface reflects the sun's energy, within the electromagnetic spectrum. In addition, spectral signatures are typically characterized on an X-axis (wavelength) and Y-axis (percent reflectance) graph so that different surfaces have different spectral signatures.
Currently there are a multitude of data, tools and software,... to access and process satellite data. The goal of this PFG would be to access multispectral information from a certain area of the planet and process it to obtain certain information such as changes in land cover, algae growth in the water, different types of crops, or the amount of urban development in a area. The specific information needed depends on the application and will be defined when the PFG starts.
The student will not start from scratch as a PFM has been defended and has made a study of the art of all existing technologies and tools.
