Offers in: Engineering in Industrial Technologies
Academic supervisor:
Ibon Elósegui Simón
CEITTecnundepartment :
Tecnun: department Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Description and Objectives:
This project an innovative solution: direct oil cooling by jet impingement on subject conductors, applied to high power density electric machines.
Using CFD simulation, we analyze how to optimize heat transfer in electric motors that will power sustainable vehicles and aircraft, reducing losses and increasing reliability.
The results will serve as a basis for the design more efficient cooling systems, contributing to the electrification of air and ground transportation.
Academic supervisor:
José Martín Echeverría Ormaechea
CEITTecnundepartment :
CEIT: Transportation and Energy Division
area :
Power Electronics, Piezoelectric Actuators, Nanometric Positioning
Description and Objectives:
Piezoelectric actuators used in high-precision positioning systems require power stages capable of supplying high voltages—typically between 100 V and 150 V—and transient currents associated with their predominantly capacitive nature. Although commercial controllers exist for this subject actuator, many have closed and limited configurations that make it difficult to optimize their performance or incorporate new specific functionalities.
The goal of project develop and validate a complete power electronics system that allows for the precise and safe excitation of piezoelectric actuators intended for positioning applications. The system must generate programmable control signals (unipolar or bipolar), operate over voltage ranges suitable for different types of actuators, and provide a dynamic response that allows for the evaluation of both the static and transient behavior of the device.
The power stage will include:
-
Implementation of voltage conversion stage to levels suitable for piezoelectric excitation (e.g., boost, flyback, or high-voltage linear power supply topologies).
-
amplification stage design capable of supplying reactive current and maintaining the linearity required for precision applications.
-
Implementation of control and modulation systems necessary to generate ramps, dynamic profiles, or sinusoidal test signals.
-
Internal sensing and monitoring of core topic parameters, such as applied voltage, instantaneous current, or system temperature.
This project students to delve deeper into the design high-voltage power converters, precision analog electronics, capacitive load control, and protection techniques, result fully functional and documented piezoelectric module .
Academic Supervisor:
Ainhoa Galarza
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT: Transport and Energy Division
subjectarea :
Industrial Automation
Description and objectives:
Power converters for automotive applications typically communicate with the outside via buses such as CAN, serial port or Ethernet. The developer can send commands and receive information from a computer to diagnose the equipment, but with very rudimentary applications. The main purpose of the project is to develop a PC application to manage communications with the converter, and at the same time interact with the test bench devices (voltage sources, oscilloscopes, etc.).
The application must autonomously execute previously programmed tests by sending sequences of commands to all the elements of the bench; allow real-time data visualization by adjusting channels, scales and units; and export data to keep a secure record of all the activity, both of the converter operation and oscilloscope waveform captures at specific times of the essay. The essay sequences will be set up in a user-friendly way in the application environment, allowing to incorporate conditional logic to adapt the test flow to the conditions detected during the execution.
All actions, errors and results will be recorded in a log system, which will facilitate the audit and follow-up of the tests performed.
Academic Supervisor:
Isabel Ayerdi - Aitor Larrañaga Jaio
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT: Materials and Manufacturing Division: Precision Laser Manufacturing group.
subjectarea :
Industrial Automation, Optical Metrology, Profilometry, Materials Characterization, Quality Control, Data Science, Artificial Intelligence.
Description and Objectives:
Optimization and control of laser processes using AI models requires vast data sets linking entrance parameters (power, scan speed, frequency, pitch, etc.) to output quality metrics. The student will collaborate in the creation of a high precision micromachining database from samples etched with various laser conditions.
The main task of the student will be the development and standardization of a methodological automation tool that interacts with the Sensofar S Neox 3D profilometer to massively and repeatably characterize laser micromachining samples. The student will have to configure and implement the routines in the Sensofar software to automate the acquisition of 3D profilometry data and the subsequent processing for the extraction of core topic metrics (depth, roughness, angles, etc.).
This process will eliminate the need for manual measurements, creating a clean, structured and robust data stream that will feed a database for AI creation. If automation is achieved quickly, the project will include a basic AI implementation phase on the data generated in Python.
Objectives:
-
Standardize and document the acquisition protocol using the SensoSCAN MMR (Multiple Measurement Routine) for the automation of the XY stage and measurement sequence.
-
Develop and implement Analysis Recipes in SensoPRO for the automatic calculation and extraction of quality metrics (roughness, depth, wall angles) from the data obtained.
-
Create the data workflow that combines the process parametersentrance) with the quality metrics (output) in a structured dataset ready for Machine Learning.
If time permits, implement a simple Machine Learning algorithm to perform the first quality prediction on the generated dataset.
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcarcel Garcia / Cristina Rodriguez
department Tecnun CEITTecnun:
CEIT - ICT Division / PTM
subjectarea :
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science, Materials.
Description and Objectives:
development of a robust software application (preferably in Python) for parameter optimization of material constitutive equations (known models in the literature).
The goal is to automate the task of fitting models to experimental data (read from Excel/CSV) to predict mechanical properties. It is required to compare different optimization algorithms to determine the best fitting strategy. The project should be integrated or be the basis of an existing application.
Proposed Activities:
-
Literature review of constitutive models and optimization algorithms.
-
Mathematical formulation of the optimization problem (error function).
-
Implementation of data reading (Excel/CSV) and constitutive equations.
-
Implementation and comparison of at least two optimization algorithms (e.g., Levenberg-Marquardt vs. Genetic Algorithms).
-
development the Username interface for loading, adjustment and display of results.
-
Validation and analysis of the effectiveness of the software and algorithms applied.
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcárcel García
department Tecnun CEIT:
ICT Division
subjectarea :
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science
Description and Objectives:
development of a Python application to automate exploratory data analysis (EDA) and predictive regression modeling.
The goal is to build a tool able to read a database (CSV/SQL), automatically classify variables (numerical, categorical), perform univariate and bivariate statistical studies (correlations, graphs) and, finally, automatically apply and compare regression models for a variable of interest. The goal is to offer a robust software for the quick start of Data Science projects.
Proposed Activities:
-
Review of AutoEDA and AutoRegression techniques.
-
Intake module : Data reading and automatic classification of variables.
-
EDA module : Implementation of statistical studies and automatic graphs (univariate and relationship between variables).
-
Regression module : Automatic preprocessing and fitting/comparison of multiple regression algorithms (simplified AutoML).
Username interface: development of an interface (e.g., Shiny) for the visualization of results and insights.
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcárcel García
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT - ICT Division
area subject:
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science
Description and objectives:
The maintenance scheduling problem, known as the Maintenance Scheduling Problem or Maintenance Scheduling Problem, consists of organizing maintenance activities within a schedule in an optimal manner. This problem seeks to minimize interruptions and operating costs by ensuring that both preventive and corrective maintenance are performed at the appropriate times.
The goal of this final Degree project is to develop an optimization tool that addresses the efficient scheduling of maintenance schedules. The tool will be developed preferably in Python, with additional Matlab or R options.
Proposed activities for the student:
Bibliographic review of the most common optimization problems and algorithms applied in maintenance scheduling.
2. Mathematical formulation of the problem, establishing the relevant criteria and restrictions.
3. Implementation of the solution using a heuristic optimization algorithm or open source solvers.
4. Analysis of results and comparison of the effectiveness of the applied approach , with recommendations for its use in different maintenance situations.
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcárcel García
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
ICT Division. Group of data analysis and Information Management
area subject:
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science
Description and objectives:
The application of time-dependent covariates in survival analysis has improved the prediction of time to default in behavioral credit scoring models. However, when these covariates are endogenous, two problems occur: estimation bias and the lack of a framework to predict the future values of the event and the covariates.
Joint models are a statistical approach that simultaneously integrates longitudinal and survival data, allowing to model the joint evolution of an event of interest (such as time to default) and endogenous time-dependent covariates. This project explores for the first time the application of discrete-time joint models to credit scoring, and proposes a novel extension by including autoregressive terms in the endogenous covariates.
The project will apply these methods to U.S. mortgage data, evaluating whether discrete-time joint models improve predictive accuracy compared to traditional survival models and whether performance is optimized by including an autoregressive term.
Proposed student activities:
-
Literature review on conjoint models and their application in credit scoring.
-
Mathematical formulation of the model set in discrete time.
-
Implementation of model in R or Python.
-
Analysis of results, comparing predictive performance against other models.
This project will allow the student to explore advanced statistical modeling techniques applied to financial data and improve predictions in the context of credit risk.
Academic Supervisor:
Dr. Carlos Alejandro Peñuelas Angulo
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT - ICT Division
subjectarea :
Information security, data analysis
Description and objectives:
The overall purpose of this project is the design and implementation of an architecture that offers data analysis functions (Machine Learning, data mining, etc.) as a service implementing mechanisms for the preservation of data privacy, also known as Privacy Enhancing Technologies (PETs). This can include from the use of advanced cryptographic mechanisms to federated learning.
The activities expected to be carried out during the execution of this project are:
-
Analyze examples of PETs applied to data analysis.
-
Design an architecture for privacy-preserving data analysis as a service.
-
Implement the architecture using state-of-the-art technologies.
Academic Supervisor:
Saioa Arrizabalaga
department Tecnun CEIT:
CEIT - ICT Division. data analysis and Information Management Group
area thematic:
Industrial process modeling. Cybersecurity.
Description and objectives:
Hybrid testbeds allow the study of offensive and defensive cybersecurity mechanisms in industrial environments and also their impact on the process under attack or to be defended.
This project would be focused on the generation of digital twins for industrial systems (e.g. wind turbines, water distribution networks...), based on existing Simulink models. The student will have to map sensors/actuators on the models, define operating states (normal, abnormal) to improve testbed monitoring and response capabilities, analyze potential system cybersecurity threats and develop mitigation strategies. Simulink models will be modified so that they can be integrated into the virtualized testbed so that they can be operated in real time.
Academic Supervisor:
Dr. Emilio Sánchez Tapia
department CEITTecnun:
CEIT - Vision and Robotics
subjectarea :
Industrial automation/robotics
Description and objectives:
This Degree final project is born as a direct continuation of a previous work in which the same unscrewing operation was successfully automated. In that first phase, the control architecture was based on a traditional industrial system, using a PLC to govern the KUKA robot. Having validated the mechanical and vision feasibility of the system, this new project focuses on exploring an alternative and more flexible control architecture.
The new goal is therefore to approach the control from two different perspectives in order to compare its performance. Instead of using the PLC, a specialized controller, extremely reliable and designed to operate in real time, the same process will be implemented using ROS (Robot Operating System) on a conventional computer. ROS is not an operating system like Windows, but a set of open source software tools that greatly facilitates the programming of robots and the integration of components such as cameras or artificial intelligence algorithms. The final scope is to evaluate and quantify the advantages and disadvantages of each approach: the robustness and determinism of the industrial PLC versus the flexibility, speed of development and processing power offered by a system based on ROS and a PC.
Tasks to be performed by the student:
-
Familiarization with previous work
-
Learning the programming technique of the Kuka Issy robot.
-
Learning to use the ROS operating system
-
Programming from ROS of the execution of a sequence of paths for screwing/unscrewing (language to be defined, it can be in Python or C++).
-
Testing and evaluation of the performance achieved
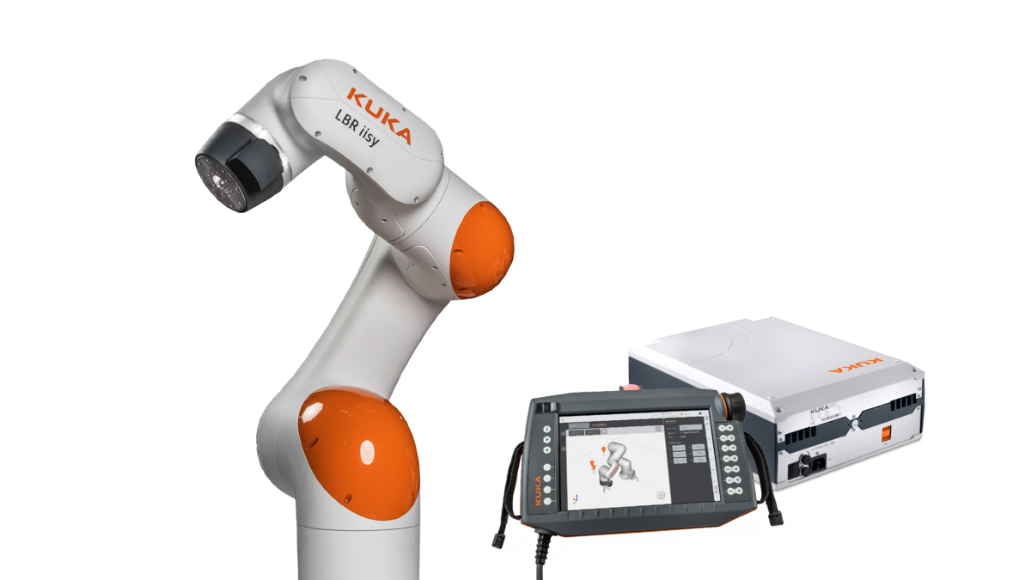

Photo of the KUKA collaborative robot to be used in the PFG.
summary:
The present Final Project Degree has as goal to perform an exhaustive analysis of the data sources and sensor systems used in Gipuzkoa to model vehicular flows. At present, the information related to this data is dispersed among different institutions, such as the Basque Government, the Provincial Council of Gipuzkoa and municipalities. This study seeks to centralize and categorize these sources, evaluating the data collection methods, the types of sensors implemented, the roads on which they operate, the percentage of vehicles they detect and the reliability of the measurements.
The results will make it possible to identify possible inconsistencies between data sources and establish a basis for comparison, contributing to improved mobility management in the territory.
Objectives:
-
Identify the data sources used by the main institutions responsible for mobility in Gipuzkoa (Basque Government, Provincial Council of Gipuzkoa, municipalities, among others). These may be their own data or data from third parties.
-
Catalog the types of sensors used (such as inductive loops, artificial vision cameras, LIDAR sensors, etc.) and their location on the network road.
-
Analyze the percentage of vehicles detected by each sensor system and the reliability of their data.
-
Compare methods and results between different institutions to identify possible discrepancies and areas for improvement.
-
Propose recommendations to optimize the integration and use of these data sources in future mobility studies.
Methodology:
-
Bibliographic and documentary review
-
Study of reports and technical documents published by the responsible institutions.
-
Analysis of rules and regulations and protocols related to vehicle data collection in Gipuzkoa.
-
-
Primary data collection
-
contact direct contact with institutions (Basque Government, Provincial Council, municipalities) to obtain information on their data sources and implemented systems.
-
Interviews with technical experts in mobility and road management.
-
-
Sensory analysis
-
Classification of sensor types according to their technology, location and functions.
-
Evaluation of the vehicle detection rate and the reliability of the data generated.
-
-
Interinstitutional comparison
-
Analysis of the differences in the data collected by each institution.
-
Identification of overlaps and gaps in data coverage
-
-
Elaboration of the final report
-
Centralization of collected information and essay of a consolidated list of data sources and sensor systems.
-
Proposals for improvement based on the findings of the study.
-
Expected results:
-
An exhaustive list of the data sources available and used in Gipuzkoa, classified by institution and technology used when applicable.
-
A detailed map of the sensors installed on the network road, indicating the roads covered and the technologies used.
-
A comparative report that identifies discrepancies and similarities in vehicle flow data between institutions.
-
Concrete recommendations to improve the integration and quality of vehicle data in the territory.
-
instructions for future mobility studies based on more consistent and centralized data.
schedule:
To be defined, according to availability.
contact person:
Zuriñe Varela(zvarela@unav.es).
Academic Supervisor:
Santiago M Olaizola
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
Materials and Manufacturing Division: Precision Laser Manufacturing group.
area subject:
Industrial manufacturing processes
Description and objectives:
Our research activity is focused on laser processing of materials. For this purpose, we use ultra-short laser pulses (femtosecond lasers), capable of producing very precise Structures on material surfaces with a very high definition of the order of micrometer. This is made possible by the "cold ablation" processing regime. High definition surface textures can be used for a variety of applications, such as friction management, plastic injection molds, implants, metrology of self-cleaning objects, antennas, etc.
The research project offered in this group covers the fabrication, measurement and modeling of the Structures for a selected application. The specific nature of the project depends on the duration of the placement and the student's background. For example:
Industrial technologies engineering: laser modification of stainless steel to control surface hydrophobicity, design and laser process programming.
Telecommunication engineering: analysis of the predictability of periodic corrugations on surfaces produced by femtosecond lasers, analysis of results, laser beam control.
Field: laser applications
requirementsPhysics: solid knowledge of physics. Python programming skills are recommended.
Academic Supervisor:
Saioa Arrizabalaga
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
ICT Division. Group of data analysis and Information Management
area thematic:
Industrial process modeling. Cybersecurity.
Description and objectives:
Hybrid testbeds allow the study of offensive and defensive cybersecurity mechanisms in industrial environments and also their impact on the process being attacked or defended.
This project would be focused on the generation of digital twins for industrial systems (such as wind turbines, water distribution networks...), using existing Simulink models. The student will have to map sensors/actuators on the models, define operating states (normal, abnormal) to improve testbed monitoring and response capabilities, analyze potential system cybersecurity threats and develop mitigation strategies. Simulink models will be modified so that they can be integrated into the virtualized testbed so that they can be operated in real time.
Academic Supervisor:
Luis Vitores Valcárcel García
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
ICT Division. Group of data analysis and Information Management
area subject:
Mathematical Optimization, Data Science
Description and objectives:
The maintenance scheduling problem, known as the Maintenance Scheduling Problem, consists of optimally organizing maintenance activities within a schedule. This problem seeks to minimize interruptions and operating costs, ensuring that both preventive and corrective maintenance are performed at the right times.
The goal of this end of Degree project is to develop an optimization tool that addresses efficient scheduling of maintenance schedules. The tool will be developed preferably in Python, with additional Matlab or R options.
Proposed student activities:
-
Bibliographic review of the most common optimization problems and algorithms applied in maintenance scheduling.
-
Mathematical formulation of the problem, establishing the relevant criteria and restrictions.
-
Implementation of the solution using a heuristic optimization algorithm or open source solvers.
-
Analysis of results and comparison of the effectiveness of the applied approach , with recommendations for its use in different maintenance situations.
Academic Supervisor:
Emilio Sanchez Tapia
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
Materials and Manufacturing Division: Robotics and Industrial Control Group.
area thematic:
Robotic Engineering
Description and objectives:
In the context of robotics in the 21st century, the concept of the connected factory arises where machines, mobile robots and humans coexist. Mobile robots may or may not include a robotic manipulator arm or MoMa (MObile MAnipulator). If there is only the mobile robot, it is usually referred to as AMR (Autonomous Mobile Robot) or AGV (Autonomous Guide Vehicle) according to its Degree of freedom in navigation (see figure below).
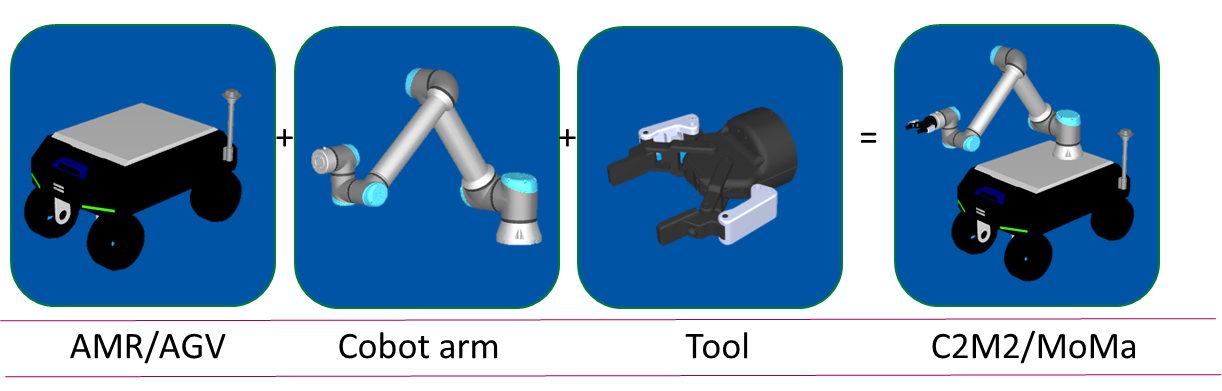
Figure 1: Constituent elements of a platform-mounted collaborative robot (or MoMa).
The main application of this device subject is to increase the level of factory automation in sectors where today automation has leave penetration, such as intralogistics and machine tending. In these scenarios, the robot can move raw materials, products in the manufacturing process or even search for machine replacement parts (such as a cutting head for a CNC). In any case, the MoMa will be able to perform the task either autonomously or as an assistant to a human operator (see figure below).

Figure 2: Factory scenario where a MoMa becomes one more resource of the factory where it can work alone or in collaboration with other human operators.
A likely scenario is that in the factory we will find more than one mobile robot, each of them with different capabilities and probably from different manufacturers. In this case it is important to have software that coordinates the tasks and distributes them appropriately according to the availability and/or capacity of each robot. Such software is known as a robot fleet manager.

Figure 3: A fleet manager coordinates the work of a set of robots.
There are many fleet management solutions on the market, but they are usually proprietary and compatible with only one brand of robot.
The goal of the final project of Degree is to deploy and test an open-source robotic fleet manager. The tests will be done both in simulation and with real robots.
As of essay of this document, it is planned to use open-rmf (Open-RMF: https://www.open-rmf.org/ ) or equivalent, see the following figure.
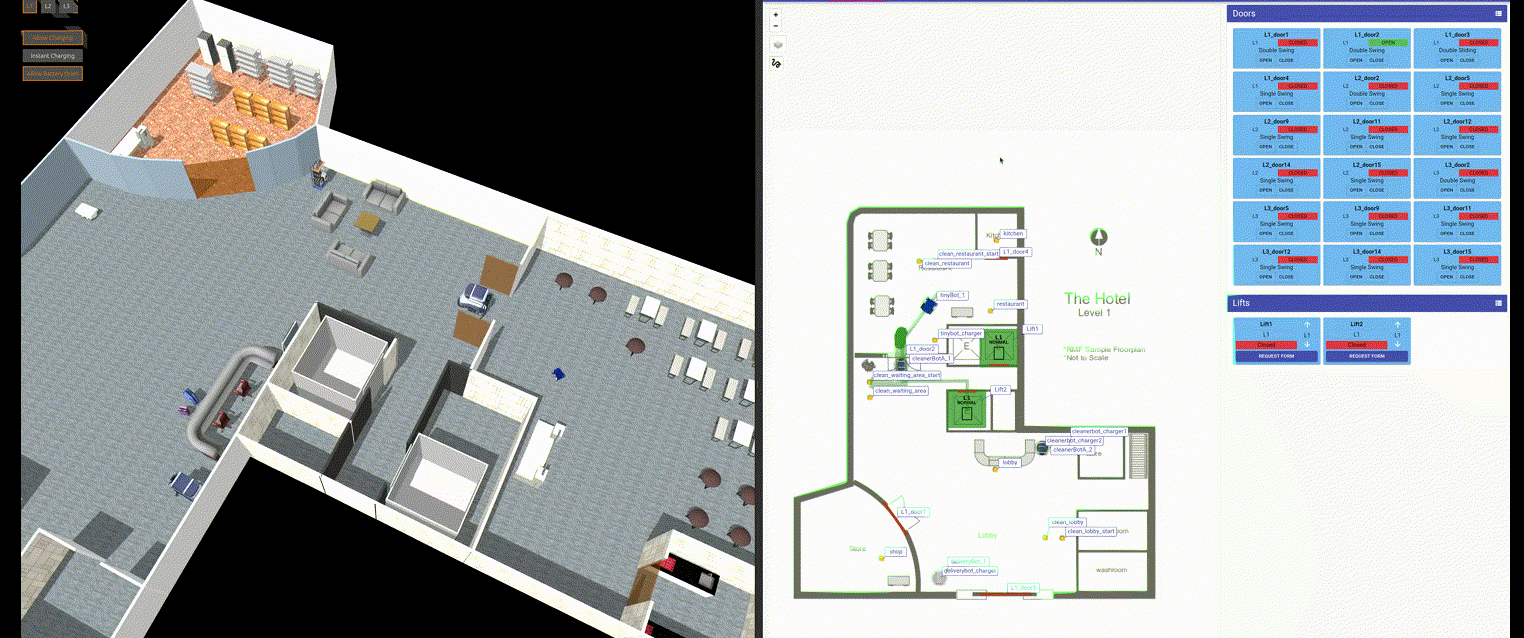
Figure 4: Screenshot of a simulation of coordinated fleets from open-rmf.
It is offered, during the execution of project:
-
Incorporation to the robotics group of researchers from the CEIT
-
Training in the software/hardware tools employed
-
Possibility of a job offer in a company in the sector.
Academic Supervisor:
Beñat Elduayen
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
Water and Waste Division
area subject:
Mathematical modeling and numerical simulation.
Description and objectives:
Mathematical modeling and simulation tools assist in design, operation and optimization of water treatment infrastructures. This project, focuses on using EPANET, a software that allows predicting the hydraulic and water quality behavior along a pipeline network .
Water distribution networks are complex and time consuming to fully simulate. The project focuses on developing an algorithm to simplify water distribution networks automatically using Python and EPANET. This simplification will allow faster simulations, which are the basis for creating tools from financial aid to real-time operation. The student is expected to apply his/her theoretical knowledge in the areas of numerical computation, mathematical modeling and programming to contribute to develop an innovative digital tool that positively impacts the sustainability and efficiency of water resources.
Academic Supervisor:
Enrique Castaño Carmona
Division CEIT:
Advance Powder Metallurgy and Laser Manufacturing Group
area thematic:
Computing, modeling and simulation
Description and objectives:
The machining of materials using ultra-short pulse lasers is a very recent technology development and opens multiple possibilities in the field of functional surfaces, such as low friction coefficient surfaces in wind turbines or anti-icing surfaces in aeronautics.
Currently, Ceit is leading a European project in which one of its objectives is to develop a simulation software for the machining process with this subject of lasers. The mathematical modeling of the process is already well advanced, as well as its numerical implementation.
The task of this PFG will be to design and develop the graphical interface with the Username of the simulation program so that its use is easy and intuitive. The student will apply and extend his knowledge of Python programming, GUI (Graphic User Interface) and design UX/UI (User Experience/User Interface) to achieve an interface that allows Username an attractive experience of the simulation program.
Academic Supervisor:
Aitor Cazón
Responsible for project
Iñigo Puente Urruzmendi
area o department from Tecnun:
Mechanical Engineering and Materials
Description and objectives:
There are several external factors that influence the mechanical behavior of materials, one of the most important of which is temperature. The goal of this work is to design and manufacture a temperature controlled chamber adaptable to the universal testing machine located at department of Mechanical Engineering and materials of Tecnun, in order to evaluate the mechanical behavior of different materials through tensile and flexural tests at different temperatures.
deadline for completion of project: June 2024.
Description and objectives:
The wood industry generates a large amount of leftover materials, both wood and components in good condition that are not currently being used or properly utilized.
This project has as goal the improvement of the circularity of the activity of the companies associated to Arozgi that work with wood, through the industrial symbiosis and the development and implementation of a Catalog of products and projects in the Circular Market platform, developed by Tecnun.
The phases that will be carried out to reach goal are as follows:
-
Analysis and identification of resources generated by the companies (products, wastes, components, by-products) but with potential value. This analysis will include both the actual resources and the identification of the best available techniques for their valorization.
-
Evaluation of these resources to facilitate their use, including them in a archive in CircularMarket.
-
design promotion and actions necessary to stimulate the use of such waste as products for other companies and the promotion of symbiosis between them.
Academic supervisor:
Carmen Jaca
area thematic:
Sustainability and Economics Circular
area o department:
Industrial Organization Engineering.
Academic supervisor:
Ainara Rodríguez - Isabel Ayerdi
Division CEIT:
Materials and Manufacturing. Advanced Manufacturing in Powder Metallurgy and Laser Group.
Description and objectives:
Laser functionalization of surfaces is an approach widely used in a wide variety of applications and sectors, as it allows to provide final products with added functionalities, including, among others, decorative effects, the ability to repel liquids or improve the adhesion of coatings. At the moment Ceit is developing an international project of research and development in this last field, whose goal is to improve the adhesion of antibacterial and antiviral coatings to high traffic objects such as handles, switches or push buttons.
In the framework of this project in cooperation, a TFG is proposed whose goal is the design and implementation of a test bench for the characterization of the surface properties of the manufactured samples, among which are the improvement of adhesion, hydrophobicity/hydrophilicity characteristics or optical properties among others. In addition to the above, it will be necessary to implement an intelligent processing system for the data obtained by the measuring elements.
Academic supervisor:
Yago Olaizola
Division CEIT:
Materials and Manufacturing. Advanced Manufacturing in Powder Metallurgy and Laser Group.
Description and objectives:
Transparent materials are currently used in a multitude of applications in which their optical properties are particularly relevant: lenses, devices for optical communications, smart glasses or optical sensors, among others. In this context, the characterization of the optical properties is a point core topic in the development of the devices.
The goal of this project will be to design and implement an optical microscopy system, starting from different optical and mechanical elements, for the analysis of certain properties of transparent materials. After the validation of the equipment, we will proceed to study the optical behavior of this substrate subject after different laser engraving processes. In parallel, it will be necessary to implement an intelligent processing system for the data obtained by the measurement devices.
Academic supervisor:
Gemma García Mandayo
Division CEIT:
Materials and Manufacturing. Advanced Manufacturing in Powder Metallurgy and Laser Group.
Description and objectives:
The project is framed within the development of an innovative system for the measurement of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and coagulation, for application in clinical diagnostics. The main purpose of the system is to provide results of ESR and/or blood coagulation in a minimum time, with a minimum amount of sample and using sustainable materials, offering significantly higher performance than the devices currently available in the market, and thus allowing a faster and earlier diagnosis of pathologies such as infections, tumors or autoimmune diseases.
The goal of project is the optimization of the sample characterization processes, developing a test bench and performing tests to improve the performance of the device.
Academic supervisor:
Leticia Zamora Cadenas - Iker Aguinaga Hoyos.
Division CEIT:
Information and Communication Technologies. Intelligent Systems for Industry 4.0 Group.
area thematic:
Telecommunication/Industrial Engineering
Description and objectives:
Indoor location systems are a booming element in recent years. Whether using radiofrequency technologies, inertial sensors or artificial vision systems, the location of objects or people in interior spaces is an element core topic in many applications (tracking of parts, access to security areas, tracking of people, augmented reality, etc.).
To determine and evaluate the accuracy of a location system, the most common method is to measure guide a number of control points or tests in a controlled environment to determine the accuracy of the system. However, this subject measurement is always subject to measurement errors, human error, and the impossibility of tracking a moving element in real time. Another widespread option, especially when the accuracy is to be evaluated dynamically, is to resort to cost-effective systems that allow the creation of the real path or "ground truth", such as, for example, vision tracking systems. However, it is not always possible to deploy this type of system subject , or the economic means to do so are not always available. Therefore, being able to evaluate the accuracy of indoor positioning systems at a low cost is still a problem that researchers and companies are trying to solve.
Currently Ceit has a line of research associated with positioning systems for indoor spaces, in which it works with various companies to provide solutions to their needs. This is why the need for a ground truth system that is easy to install and not too expensive was born.
The task of this GFP would be to develop a ground truth system, using virtual/augmented reality systems, for subsequent use in evaluating the accuracy of the proprietary indoor location system Ceit. HTC Vice, Oculus Quest and Hololens 2 hardware are available for the development of this system using the Unity3D programming platform. The candidate must have programming skills in C# or similar languages such as C++ or Java.
Academic Supervisor: Miguel Martínez-Iturralde.
Division CEIT: Electric Vehicle and Smart Grids.
area subject: Electrical Engineering.
Description and objectives: In recent years there has been an exponential growth in aeronautical applications related to small electrically propelled vehicles: drones, flying taxis, vertical take-off vehicles (VTOLs), etc. In order to obtain electric flying vehicles with a practical range, it is essential that the weight of their components be kept to a minimum. In the case of electric motors, this means increasing the power density above the values of current solutions.
In this PFG we want to design a high power density motor for application in drones and small electric aircraft. The student will handle professional tools for the design and simulation of electrical components and will work in all the areas involved in developing a system: electromagnetic, thermal, mechanical, etc.

Academic Supervisor: Miguel Martínez-Iturralde.
Division CEIT: Electric Vehicle and Smart Grids.
area subject: Electrical Engineering.
Description and objectives: The development of hybrid and all-electric aeronautical applications is a reality, with numerous projects that have demonstrated on a small scale the feasibility of a quieter and more environmentally friendly aeronautics. In this sense, the major players in the electric sector (Airbus, Boeing, Rolls-Royce, etc.) are devoting great efforts to the electrification of commercial aircraft.
One of the challenges for the development of electrically powered aircraft is related to the design of high voltage electrical insulation systems that can operate at high altitudes, where air pressure is minimal and the risk of electrical discharges is higher. Currently, Ceit is involved in a European project to develop insulation systems that will be applicable in tomorrow's electric aircraft.
The task of this PFG would be to simulate aircraft electrical systems using commercial finite element software and obtain criteria from design for subsequent application to electric aircraft.

Academic Supervisor: framework Satrústegui.
Division CEIT: Electric Vehicle and Smart Grids.
area subject: Electrical Engineering.
Description and objectives: The noise generated by electric motors is becoming increasingly important due to the fact that it is embedded in systems where comfort is a very important aspect (e.g. electric cars). In this sense, this PFG tries to characterise the noise in an electric motor by performing a multiphysical analysis, starting by characterising the machine at an electromagnetic and thermal level and then developing a mechanical analysis that results in obtaining the noise generated at different levels of torque and rotational speed.

Academic Supervisor: Jesús Paredes.
Division CEIT: Electric Vehicle and Smart Grids.
area subject: Electrical Engineering.
Description and objectives: During the last decade, many of the aircraft auxiliary systems (pneumatic, hydraulic and mechanical) have been replaced by electric or hybrid actuators, due to incentives for the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and the reduction of operation and maintenance costs. This has led to a considerable increase in the electrical power installed in aircraft.
Traditionally, the turbines were started by a pneumatic system and the energy needed to power the aircraft's electrical systems was produced by generators coupled to the turbines. Today, the two systems have converged into a single electrical machine capable of working as both an engine and a generator. These systems include aircraft turbine starter/generators. The increasing demand for electrical energy and the limited space for starter/generators make it necessary to increase the power density of these machines.
The size, and therefore the weight and cost, of an electrical machine is primarily determined by the heat extraction and temperature limit of the materials used in its manufacture. Oil cooling systems have promising characteristics. Among all the oil cooling systems (spray, oil-dripping...), we intend to address in this project the oil-flooded stator systems.
The goal of this project is that the student are familiar with simulation tools fluid and cooling systems and to draw conclusions in order to optimize oil cooling systems for aircraft engines.
Academic Supervisor: Gurutz Artetxe.
Division CEIT: Electric Vehicle and Smart Grids.
area subject: Electrical Engineering.
Description and Objectives: Induction heating is an efficient and fast method of generating heat. It can be employee in various applications where tempering, brazing or melting of metals is required. CEIT is interested in developing computational tools (based on a set of previously developed tools) for use in the design of induction heating systems for formwork. The goal of this project is to model the electromagnetic and heating behavior of a formwork heating system and to perform optimization studies with them in order to carry out the design of a practical case.

summaryThe goal of project is the development and fabrication of a directed illumination system. This system will be mounted on a camera and will allow to record the specimens at the same time as they are mechanically tested. The system to be developed has to illuminate the specimen to be filmed from several points simultaneously. Likewise, it must be possible to modify the light sources in guide by means of an arduino. During the project , parts have to be designed and manufactured by 3D printing, LEDs have to be mounted on the manufactured parts and an arduino has to be programmed and connected to be able to control the switching on and off of the light sources.
profile of the student: Ideally a student of design, industrial technologies, mechanical or biomedical engineering. Experience in arduino programming and design 3D CAD would be an asset.
Application: Send CV, along with academic record and a paragraph of about 300 words of motivation explaining the suitability of your profile for the realization of this project.
Supervisor of project: Dr. Javier Aldazábal
deadline and resolution: Students who wish to apply must do so before the end of October and the selection of candidates will be made in November in order to start in December or January.
-
Academic Supervisor: Luis Matey
-
Title: design of a laparoscopic device for large tumor operations.
-
area/department Ceit /Tecnun:
department of Mechanics / Area of design -
profile recommended: Mechanical Engineering, design and development Product Engineering, Industrial Technologies Engineering, Biomedical Engineering.
-
Description and Objectives:
The project aims to analyze and propose alternatives for aspirations of large tumors using minimally invasive techniques. The scope of the project aims to prospect and proposal of a design that allows the tumor to be sealed with guarantees (without rupture) so that it can be aspirated without loss of tumor cells.
-
area/department Ceit /Tecnun/ :CEIT - Vision and Robotics
-
Title: Image analysis for dimensional control of industrial parts
-
Academic Supervisor: Diego Borro
-
profile recommended: Industrial Technologies Engineering
-
Description and Objectives:
The goal of the project is to analyze in 3D industrial parts to reconstruct the geometry and make a dimensional control (check if the geometry meets the designed tolerances). Before analyzing the image, it will also be necessary to study the specific application to choose the optimal hardware components (luminaire, optics, laser and camera). -
Offer active only when laboratories can be attended in person.
-
area/department Ceit /Tecnun/ : CEIT - Vision and Robotics
-
profile recommended: Industrial Technologies Engineering
-
Academic Supervisor: Diego Borro
-
Title: Image Analysis for Defect Detection in Industrial Parts
-
Description and Objectives:
The goal of the project is to make use of the tool Inspect Express (from Teledyne Dalsa) to analyze in 2D industrial parts and find defects. This tool allows to program the image analysis algorithms in a visual way through its graphical interface. Before analyzing the image, it will also be necessary to study the specific application to choose the optimal hardware components (luminaire, optics and camera). -
Offer active only when laboratories can be attended in person.
-
area/department Ceit /Tecnun/ :area of Mechanics of Materials - CEIT
-
area subject: Mechanics of Materials
-
profile recommended: Industrial Technologies Engineer
-
Academic Supervisor: Nerea Ordás
-
Title: Development of Copper matrix composites reinforced with Graphene, with increased thermal conductivity. Screening of manufacturing routes.
-
Description and Objectives:
The objective of this Project is to explore different manufacturing routes of Cu matrix composites reinforced with different kinds of graphene produced by Graphenea, to obtain a copper based material with improved thermal conductivity in the in-plane direction, compared to pure Cu metal. Such manufacturing routes will be based in the powder metallurgy route: mechanical alloying/mixing of powders, moulding and sintering by hot press.
Coating of graphene with certain elements to improve the thermal conductivity of the Cu-graphene interface will be also explored.
-
area/department Ceit / Tecnun: area of Thermal and Fluid Engineering - department from Mechanical Engineering (TECNUN)
-
area thematic: Mechanical Engineering
-
profile recommended: Degree en Ingeniería en Tecnologías Industriales, Degree en Mechanical Engineering, Degree en Ingeniería en design Industrial y development de Productos
-
Academic Supervisor: Gorka Sánchez Larraona
-
Title: Simulation of flow and heat transfer in curved ducts. Application in the cooling of gas turbine blades.
-
Description and Objectives:
The project consists of studying the flow and heat transfer that occurs in circular and square section ducts when they are bent 180º forming a U. For this purpose, three-dimensional simulations will be carried out using the ANSYS Fluent code and the results obtained will be compared with experimental measurements. The case in which the ducts rotate at high speed with respect to an axis will also be considered. This case has a direct application in the cooling of gas turbine blades.
-
area thematic:
Materials -
area/department Ceit /Tecnun:
department of Materials - Ceit -
Description and Objectives:
When generating virtual microstructures to perform computational simulations of polycrystalline materials it is very common to use a splitting (or tessellation) of the Issue to be simulated using Voronoid techniques. This tessellation subject is usually done by randomly placing seeds to define the grains. This total randomness produces unequal equiaxed grains. The present project aims to study the randomness-size distribution relationship. The results of the project will allow the generation of polycrystalline materials with predefined grain size distributions, and not random, as is usually the case. It will also be possible to generate inhomogeneous grains, with elongated or flattened shapes. -
profile recommended:
Given the nature of project, it is recommended for any profile as long as you have some basic programming knowledge. -
Academic Supervisor:
Javier Aldazabal Mensa -
Title:
Study of grain size distributions in three-dimensional Structures using Voronoid tessellations.
-
area thematic:
Materials -
area/department Ceit /Tecnun:
department of Materials - Ceit -
Description and Objectives:
There is currently an interest in the use of magnesium particles in the reinforcement of materials employee for bone tissue regeneration. The geometry of these particles is not spherical, which makes it necessary to be able to replicate these geometries in a computer in order to simulate the behavior of the material.
The goal of the project is the geometrical study and the generation of an algorithm capable of generating non-spherical particles, as well as the study and obtaining of their geometrical characteristics. -
profile recommended:
Given the nature of project, it is recommended for any profile as long as you have some basic programming knowledge. -
Academic Supervisor:
Javier Aldazabal Mensa -
Title:
Generation of non-spherical geometries for the simulation of Magnesium reinforced composite biomaterials.
Academic supervisor:
Andoni Irizar
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
CEIT. Materials and Manufacturing Division
area thematic:
Electronic systems
Description and objectives:
In today's industrial processes it is increasingly necessary to monitor the manufacturing process and the quality of the components resulting from the process. There are a wide variety of methods that allow such monitoring in real time, that do not require separating the parts from the rest for analysis and that do not damage the parts in the process. The most commonly used inspection techniques are those using electromagnetic fields, ultrasonic signals and machine vision. This project deals with ultrasonic techniques. The Ceit has its own ultrasonic signal test bench that allows to generate and capture ultrasonic signals in a simple way from a PC. The goal of project will consist of making a proposal of design of a miniaturized test bench (for example, the size of a Raspberry). As a comparison, the current design occupies the size of a Desktop computer. It would involve making a block diagram of the system, making a selection of components including the processing platform to be used and the components of the power source . Finally, it will be necessary to estimate the consumption and cost of the final equipment.
Academic supervisor:
Jorge Juan Gil.
department Tecnun/Division CEIT:
CEIT. Intelligent Systems for Industry 4.0 Group.
area thematic:
Systems and Control Engineering
Description and objectives:
So far the control concepts are shown on the blackboard, by means of simulations or with videos. For the Control Engineering subject we want to build a mechanical control system (two pendulums coupled with springs) to be used for teaching purposes: to show in class the different behavior of the system before several controllers. To ensure portability, the system will be controllable through USB by means of an ARDUINO card . In a previous project the mechanical system has been built. In the proposed project several controllers will be programmed in C, in particular, a proportional-integral (PI) controller that allows "teleoperation" (that the Username moves one of the pendulums and the other one follows its movement without error in permanent regime).
The Structures lattice are Structures formed by struts with various applications in the aeronautical, aerospace or biomedical sector among others. These Structures are manufactured by Additive Manufacturing due to their complex geometry and dimensions (strut diameter: 0.2 to 0.5 mm).
However, there are a number of geometric imperfections during the manufacturing process. Instead of taking these geometric imperfections into account, another common practice is to consider these imperfections in the model of the material. This requires strut testing to obtain that model of material that takes the imperfections into account.
The goal of this project is to design and manufacture the necessary tools for tensile testing of these struts with different diameters.
